Introduction to Visual Basic for Applications (VBA)
Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is an easy programming language that provides a great start to application creation for programmers who want to work entirely in the Windows system. It is Microsoft’s official programming language for programs like PowerPoint, Word, and Excel.
With VBA, we may instruct the system to start doing a single operation or a series of related activities.
A macro is a string of letters that produces a different string of characters as its output. When entered, it carries out a certain set of computational operations.
Read More: Introduction to VBA Features and Applications
How to Access VBA in Excel
STEPS:
- Ensure that you have the Development tab in your excel ribbon.
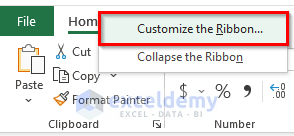
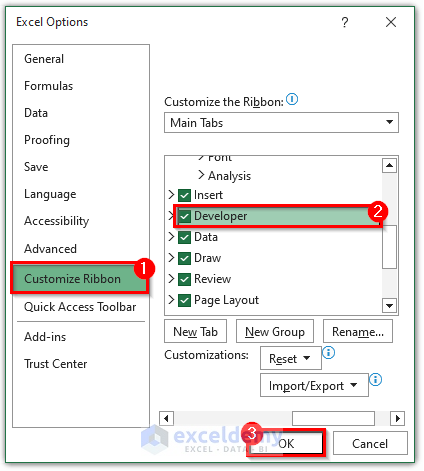
- To show the Development tab in the Excel spreadsheet, right-click on the menu bar and go to Customize the Ribbon.
- The Excel Options dialog box will appear.
- Go to Customize Ribbon and checkmark Developer.
- Click OK.
- The Developer tab will be added to the ribbon.
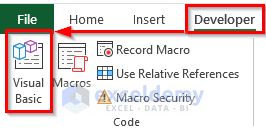
- To enter the VBA code in excel, go to Developer.
- Click on Visual Basic from the Code category to open the Visual Basic Editor. Or press Alt + F11 to open the Visual Basic Editor.
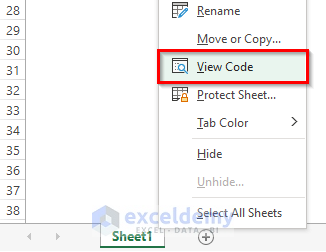
- You can also right-click on your worksheet and go to View Code. This will also take you to Visual Basic Editor.
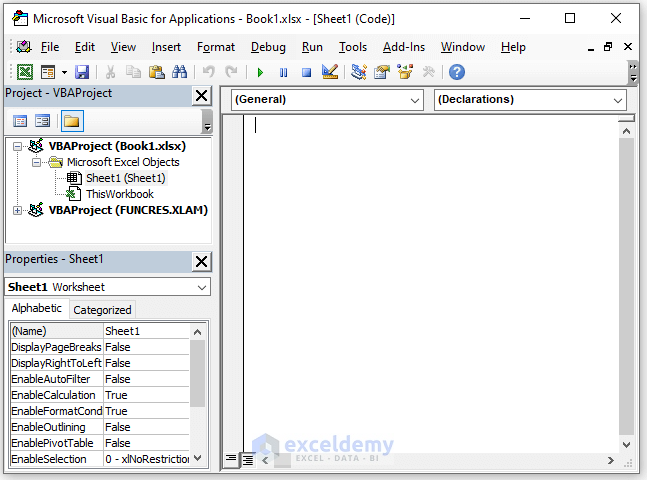
- The following window will appear in the Visual Basic Editor, where you can enter the codes. This is for the single sheet.
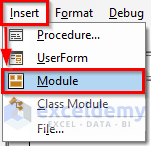
- If you want to work on the whole excel sheet, you need to click on Module from the Insert drop-down menu bar.
- This will create a Module in your workbook.
- Run the code by clicking on the RunSub button or pressing the keyboard shortcut F5.
Difference Between VB and VBA
The key distinction is that VBA focuses on coding in Office software like Word, Excel and Outlook whereas VB can create independently compiled code. While VBA is only completely generated and needs a translator to run, VB is entirely generated. As opposed to VBA, VB is written in Visual Studio; you may choose between using VB 6.0 which has a syntax quite similar to that of VBA, or Visual Basic which is more modern and designed to work with them. The most recent computer software uses the Net Framework. While VBA interfaces and packages never operate separately; rather, they operate on underlying host programs, Visual Basic may convert to a standalone executable file.
VBA Terms
1. Module
Excel saves the VBA code in a module. One of the areas of the Visual Basic Editor is the Projects Navigator, which contains details on the modules in a workbook. Modules are frequently referred to as basic functionality, and they can all be installed in a subdirectory called modules.
2. Objects
The majority of code in VBA are used to manipulate objects. Workbooks, worksheets, cells, cell ranges and cell typefaces are examples of objects. We frequently chose objects or use them as references while writing VBA code. The ‘ActiveCell’ programming language, for instance, may be used in VBA code to modify the spreadsheet object that is now chosen. You may design a procedure that starts up whenever a bar chart is changed.
3. Procedures
We know that the portion of a computer program is the procedure that carries out a certain job. The code section that begins with a statement and ends with end declarations. In VBA, there are two different kinds of procedures: function procedures, which do calculations and return a result, and sub procedures, which constitute an action in Excel and start with the word ‘Sub’.
4. Statement
A statement is a command that divides into two categories. A declaration statement, for example, uses to provide the value of a constant or variable. We take a certain action code that specifies as an executable statement.
5. Variables
Variables are storage spaces for specific things. They serve to save certain variables that change when VBA scripts are run. For instance, the ‘FirstName’ variable can be empty. The variable gives the FirstName variable and the value ‘Ayon’ when the user enters their name. Variables in coding may vary in various circumstances, just like variable costs may alter over time.
6. Logical Operators
The operations that provide enhanced processing and analytical capabilities are known as logical operators. They are little pieces of code that let a computer comprehend and evaluate things. For instance, VBA can determine if the name of the user above is ‘Mary’. The software may evaluate the input using the logical operators ‘if, then,’ ‘true,’ and ‘false.’
How Different Is VBA from Other Programming Languages: 8 Reasons
Reason 1 – Easy to Learn
VBA is easy to learn in comparison to other coding languages. All Microsoft Office apps are put in this elementary programming language. The simple characteristics of VBA make learning the application easy for aspiring users.
Reason 2 – No Installations Requirement
VBA doesn’t require any other application, unlike other programming languages. Microsoft Office already have it completely integrated. Because of this, VBA is an affordable automation tool for its customers.
Reason 3 – Useful in a Frequent Range of Industries
Many organizations continue to use Excel Online. VBA is still necessary for many businesses. This program can be useful for several businesses, like banking, logistics and inventory management and data analytics.
Reason 4 – Options for Flexible Jobs
You have the option of working full- or part-time as a VBA programmer. You may be able to locate, flexible employment choices with this expertise, such as short-term tasks or ongoing collaborations. Creating a VBA system is required for some data analysis operations. As a result, organizations that recruit data analyst jobs may demand VBA expertise.
Reason 5 – Good Professional Community
Understanding VBA gives you an additional tool in your programming toolkit. You may obtain assistance in your learning process from a network of helpful experts who are familiar with VBA. These folks have first-hand knowledge from their experience working for businesses that automate routine tasks with VBA.
Reason 6 – Automate Repeating Procedures
This procedure automates with VBA so that it can repeat and execute promptly whenever needed. Using Excel’s built-in macro recorder, several steps of the process quickly capture as macros. Other components call for hand coding and more in-depth understanding (aka programming). But in one way or another, VBA can automate all of this.
Reason 7 – Create Custom Applications
In Microsoft Access, whole programs create by default. Of course, automating operations in other Office apps have overlap with this. The user interface is the main distinction between a bespoke application and a macro. Even though a custom application is operating within the framework of a Microsoft Office host program, it still has its own user interface that users will interact with on a regular basis, if not exclusively.
Reason 8 – Study Process Analysis and Design
By investigating and evaluating the inputs and outcomes of a process and figuring out what must occur in between to convert the input to output, you can hone your analytical abilities. This information relates to a single, tiny subprocess that turns into a single macro or procedure in your VBA code. To get the intended outcome, you must also consider how to split, merge or link a number of this specific sub. There will be a lot of these operations in a large bespoke program that planners and manages to function properly together.
Download Practice Workbook


