In this article, we will learn how to analyze data in Excel, including:
- Different Excel functions, such as VLOOKUP, INDEX-MATCH, SUMIFS, CONCAT, and LEN functions.
- Using Excel charts – learn how to create various chart types, customize them, and interpret the insights they offer, and how to apply conditional formatting effectively for data analysis purposes.
- Creating pivot tables, performing calculations, and generating insightful reports.
- Using Excel’s sorting and filtering capabilities.
- The What-If Analysis feature in Excel and explore different scenarios by changing input values and observing the resulting outputs.
- Implementing data validation techniques to maintain data accuracy.
- The benefits of using tables and the built-in Analyze Data feature in Excel, which provides insights and recommendations based on your data.
- Introducing the Analysis ToolPak add-in, which offers a wide range of statistical functions and tools, including descriptive analysis and ANOVA (Analysis of Variance).
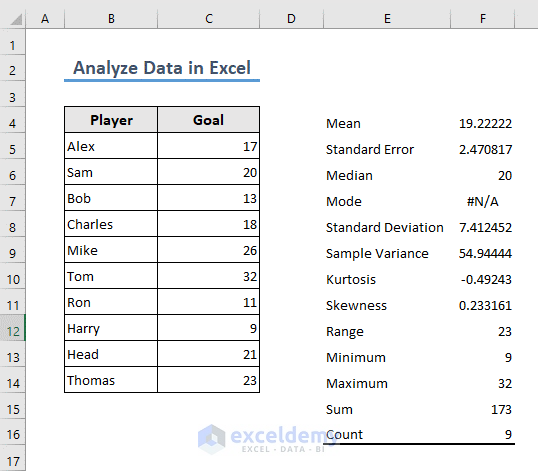
Let’s use the following dataset as a demonstration of analyzing data in Excel.
Download Practice Workbook
Download the workbook and practice.
How to Analyze Data in Excel
Method 1 – Use Excel Functions to Analyze Data
Case 1.1 – The VLOOKUP Function
The VLOOKUP function is a frequently used function for looking up any particular data from a dataset. In the following example, we want to know how many goals an individual (for instance, Alex) has scored.
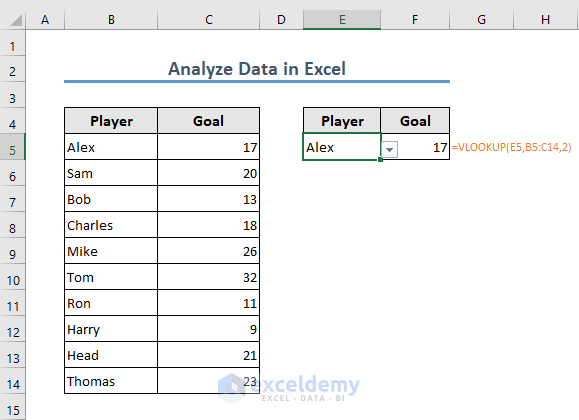
- The formula in cell F5 is
=VLOOKUP(E5,B5:C14,2)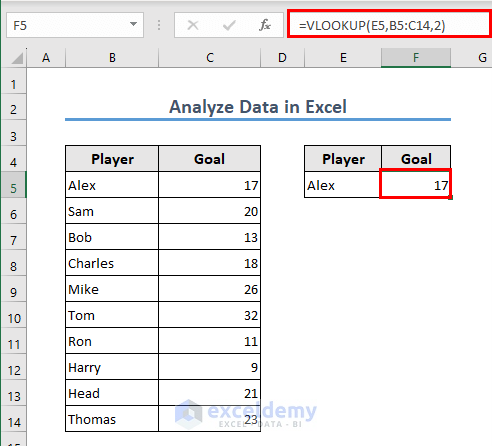
Here, Excel is looking for the value in cell E5 within the range B5:C14 and retrieving the corresponding value from the second column of that range.
Case 1.2 – INDEX and MATCH Functions
- The formula in this case is:
=INDEX(B5:C14,MATCH(E5,B5:B14,0),2)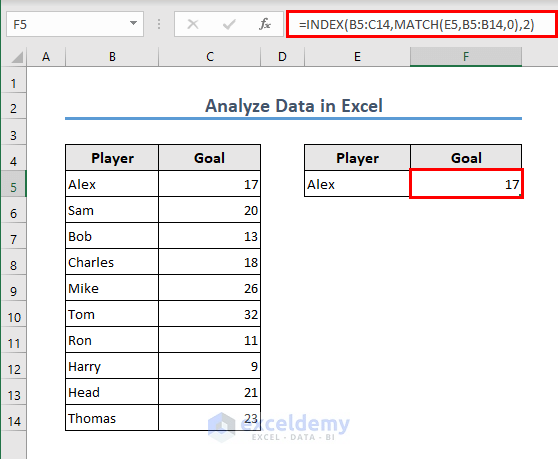
Formula Breakdown
MATCH(E5, B5:B14, 0) → The MATCH function searches for the value in cell E5 within the range B5:B14. The 0 as the third argument indicates an exact match.
Output: 1
INDEX(B5:C14, MATCH(E5, B5:B14, 0), 2) → This becomes,
↪ INDEX(B5:C14, 1, 2) → This portion retrieves the value that is in 1st row and 2nd column of the range B5:C14.
Output: 17
Case 1.3 – The SUMIFS Function
The SUMIFS function gets the sum of a range of cells with a set of conditions.
- If you want to get the goals scored by the players from Group A and Group B separately, the formula you can use in cell G5 is:
=SUMIFS($D$5:$D$14,$C$5:$C$14,F5)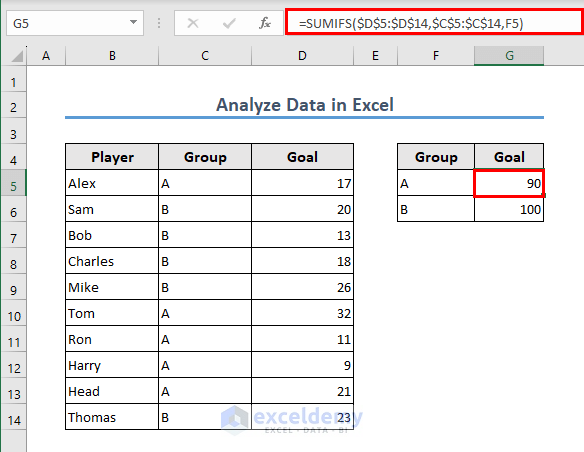
The formula sums the values in the range $D$5:$D$14 but only includes values where the corresponding cells in the range $C$5:$C$14 match the value in cell F5.
Case 1.4 – The CONCAT Function
Let’s join the first and last names of certain individuals here using the CONCAT function in Excel.
- The formula in cell D5 is:
=CONCAT(B5," ",C5)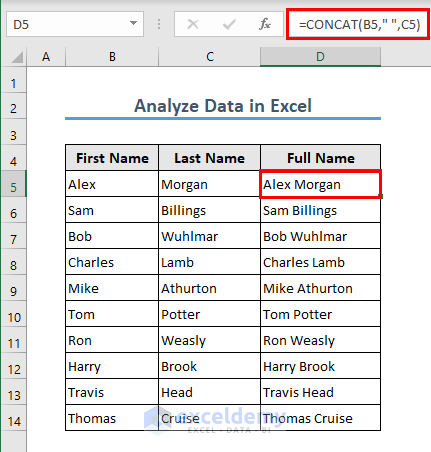
The formula joins the values in cells B5 and C5, with a space between them, resulting in a single combined text string.
Case 1.5 – The LEN Function
You can count the number of characters of a cell or an array using the LEN function.
The formula in cell E5 is:
=LEN(D5)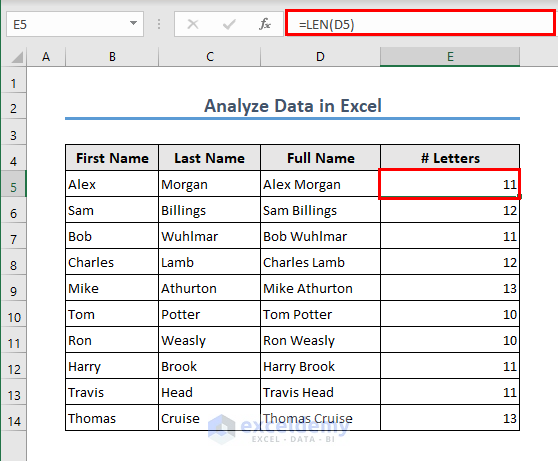
Method 2 – Data Analysis Using Excel Charts
- Select the range F4:G6.
- Go to the Insert tab and select any column chart.
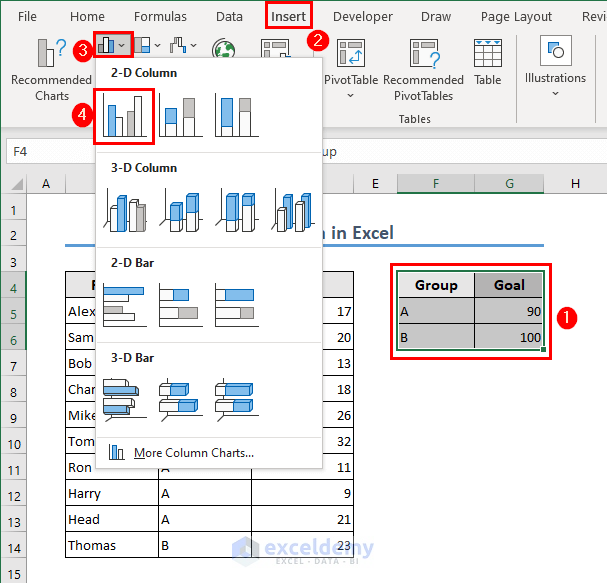
- Excel will create a column chart for you.
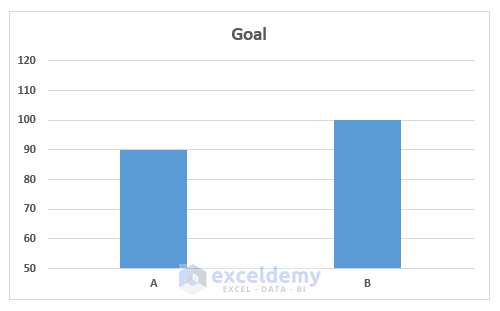
Method 3 – Apply Conditional Formatting to Analyze Data
- Select the dataset in the range C5:C14.
- Go to the Home tab and choose Conditional Formatting, then select a set of Data Bars.
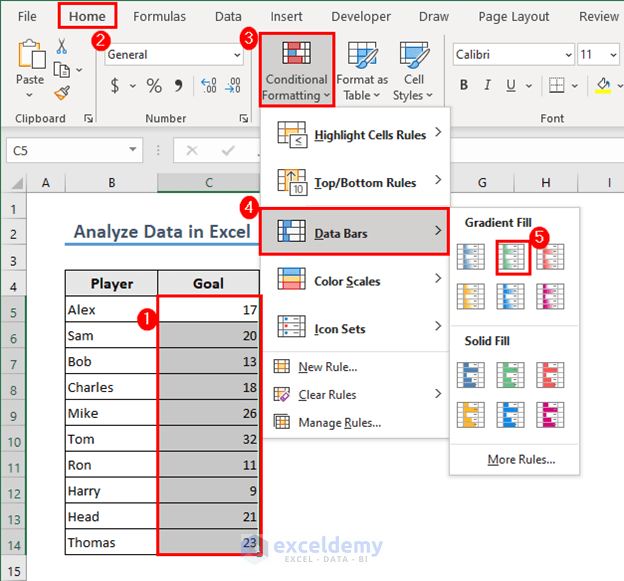
- Excel will add data bars.
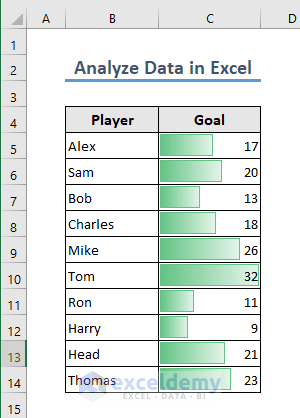
Method 4 – A Pivot Table
Let’s calculate the number of goals scored by Group 1 and Group 2 players using the Pivot Table.
- Select the dataset in range B4:B14.
- Go to the Insert tab and select PivotTable.
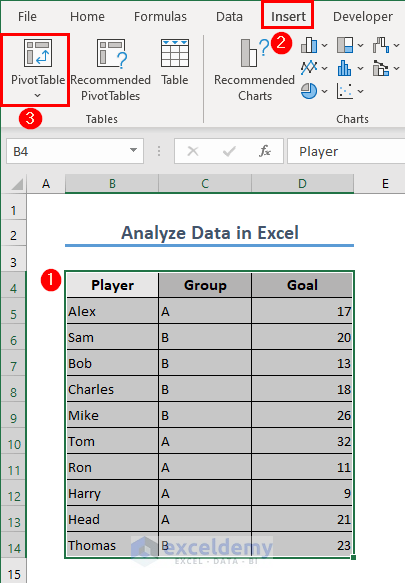
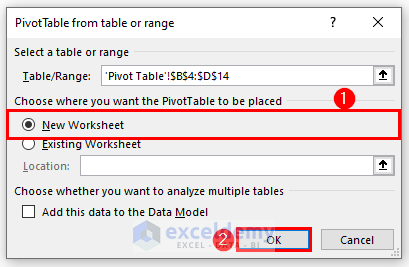
- A box will appear. We have chosen a New Worksheet as the destination of the Pivot Table.
- Drag the fields in the areas (Group in Rows and Goal in Values) shown in the image.
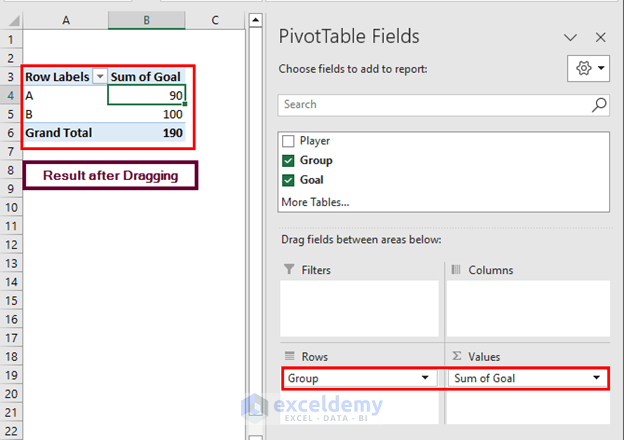
- Excel calculates the sum of goals.
Method 5 – Sorting Data in Excel
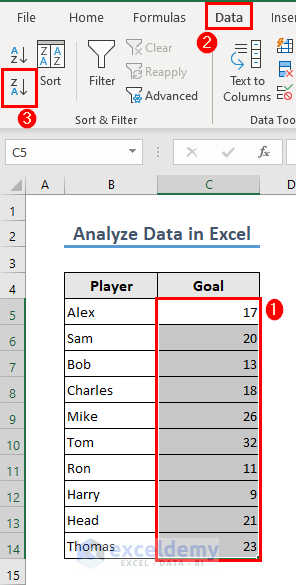
Suppose you want to sort the dataset in a descending order (Largest to Smallest).
- Select the range C5:C14.
- Go to the Data tab and select the Sort Z to A icon for descending order.
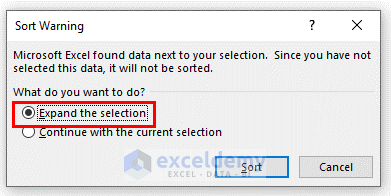
- Select Expand the selection option from the warning window.
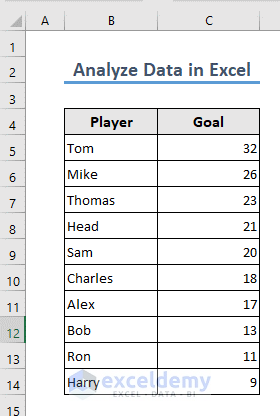
- Your data will be sorted.
Method 6 – Filtering Data in Excel
Suppose you want to see the performance of the players of Group A.
- Select range B4:D14.
- Go to the Data tab and activate the Filter option.
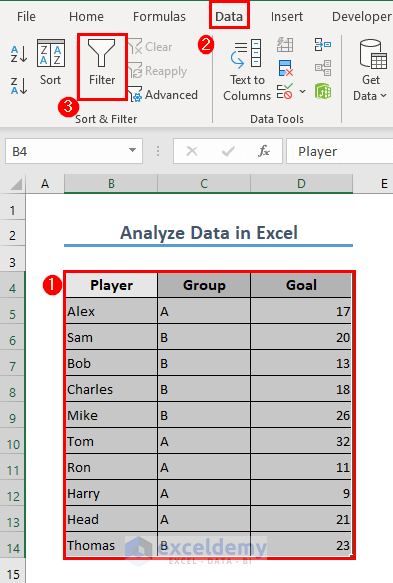
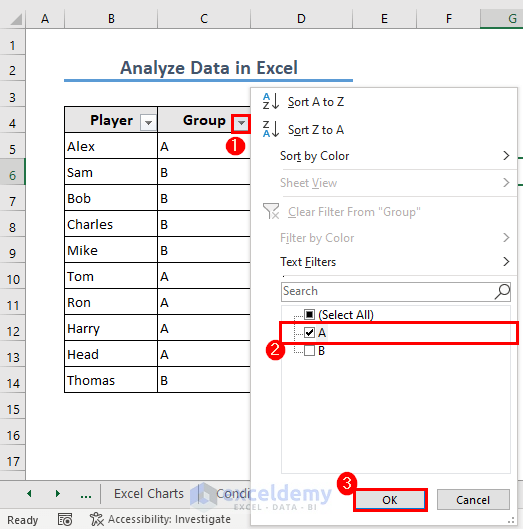
- Filter your dataset from the drop-down icon in the column heading. We have selected Group A in the Group column.
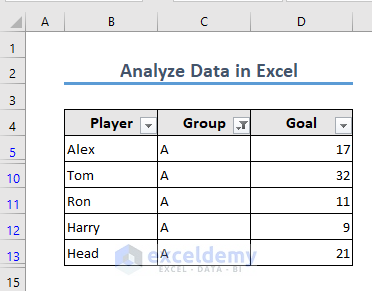
- Excel will get the list of all Group A players and their performance.
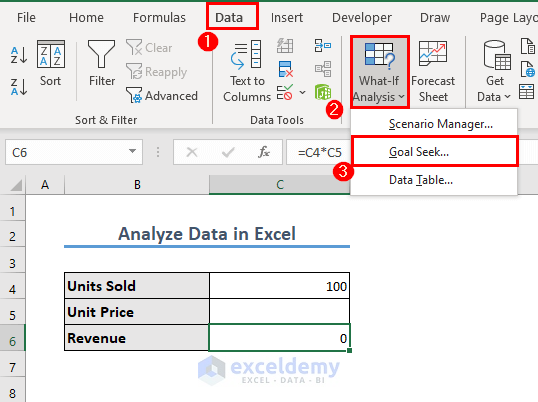
Method 7 – Excel What-If Analysis Feature
What-If Analysis in Excel refers to a set of tools and techniques that allow you to explore different scenarios and observe the potential impact on the results of your formulas or models. Excel provides several features for performing what-if analysis, including:
- Data Tables: Data Tables allow you to create a table displaying multiple results based on input values. You can perform either one-variable or two-variable data tables to see how changing inputs affect the final results.
- Goal Seek: Goal Seek helps you determine the input value needed to achieve a specific result. You specify a target value, and Excel automatically adjusts the input value until it reaches the desired outcome.
- Scenario Manager: Scenario Manager enables you to create and compare different sets of input values for your model. You can define multiple scenarios with varying inputs and switch between them to see the impact on the calculated results.
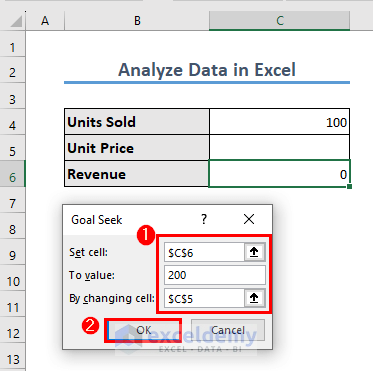
We will show an example of the Goal Seek feature. Suppose you have 100 units of a product to be sold. You want to see the necessary unit price if you want to get a revenue of $200.
The formula in C6 is:
=C4*C5This is very simple as we all know that the unit price will have to be $2. However, the fun with this Goal Seek feature is that you do not have to manually put the unit price. Rather, Excel will find it for you.
- Go to the Data tab and select What-If Analysis, then select Goal Seek.
- You want the revenue (To value) to be $200 and get the unit price in cell C5. So, the Set cell is C6 and the cell for By changing cell is C5. Put those values in the dialog box and click OK.
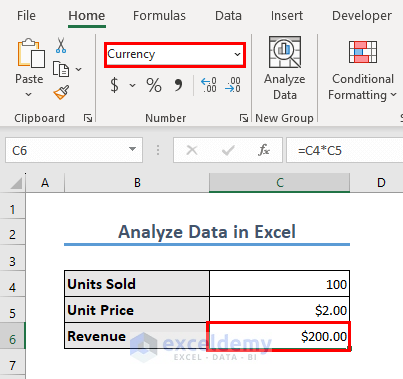
- Excel will put the unit price in C5. Put the Revenue in the currency format if you want.
- Modify the Units Sold value and repeat the process to see how it affects the result.
Read More: How to Perform Case Study Using Excel Data Analysis
Method 8 – Data Validation
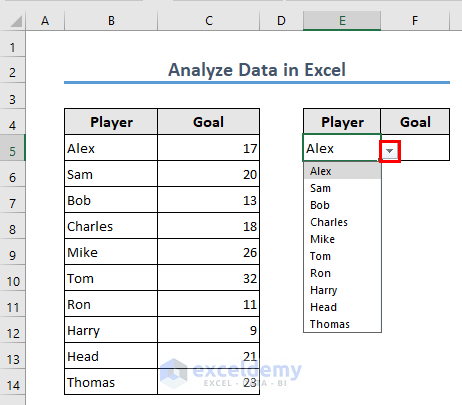
Let’s get back to our previous example (from the VLOOKUP section). We want to select a player’s name from all the available options rather than manually typing their names.
- Select cell E5.
- Go to the Data tab and select the Data Validation option.
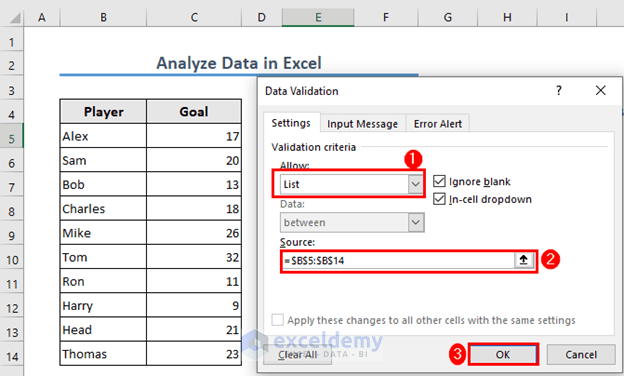
- A Data Validation box will pop up. Choose List in the Allow field.
- Set the source to =$B$5:$B$14.
- Click OK.
- You can now select the names from the drop-down icon.
- Once you select a name, you will get the number of goals the player scored.
Method 9 – Excel Table
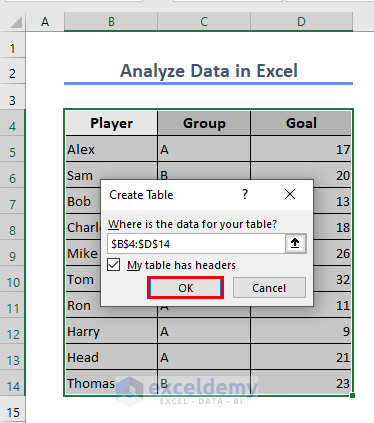
- Select the dataset in range D5:D14.
- Press CTRL + T.
- Click OK.
- Excel will create a table.
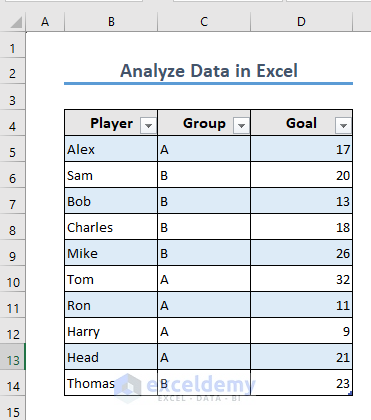
Let’s see how you can get the total goals scored by these players without using any Excel Function.
- Click on any cell of the table.
- Go to the Table Design tab (this tab will be seen only if you select a cell of the table first).
- Select Table Style Options and check the Total Row box.
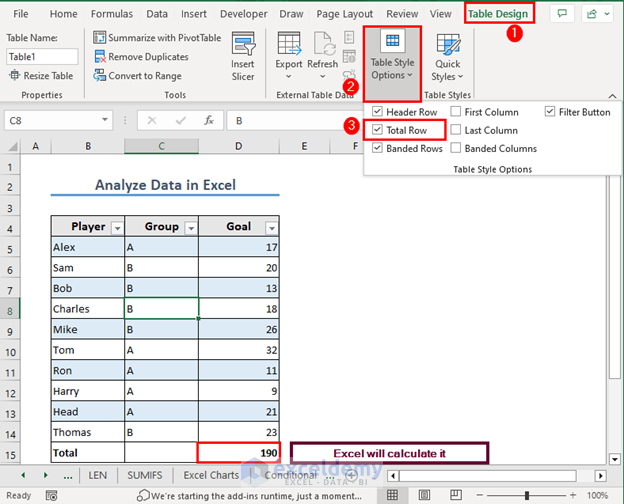
- Excel shows the total goals scored.
Read More: How to Analyse Qualitative Data from a Questionnaire in Excel
Method 10 – The Analyze Data Feature
- Add this feature to your ribbon. Put the cursor on the Home ribbon and right-click, then select Customize the Ribbon.
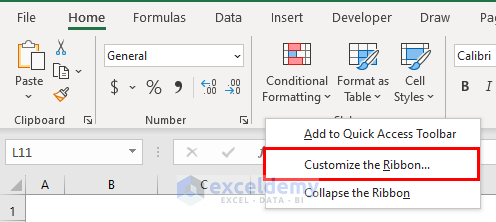
- Select New Group and set its position on the Home ribbon.
- Select All Commands and add Analyze Data to this newly created group.
- Click OK.
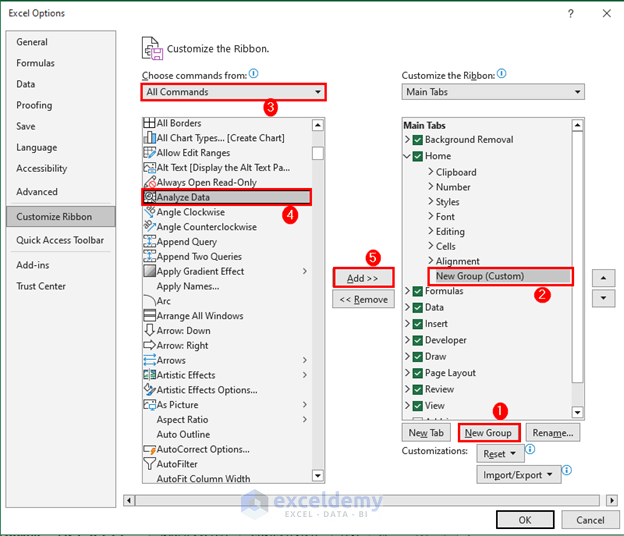
- Go to the Home tab and select Analyze Data.
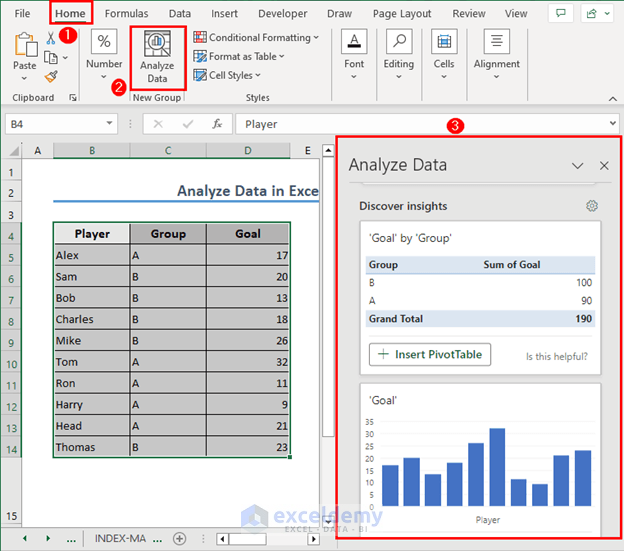
- Excel will recommend several options for data analysis.
Method 11 – Using the Analysis ToolPak Add-in
- Go to the File tab and select Options. The Excel Options box will open.
- Go to Add-ins and select Excel Add-ins in the Manage field, then click Go.
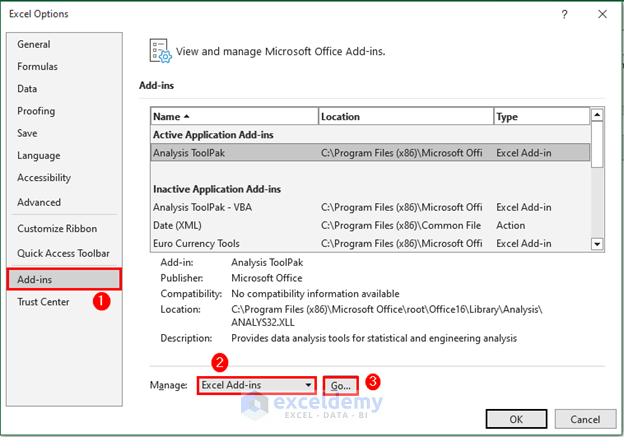
- Check the box for Analysis ToolPak and click OK.
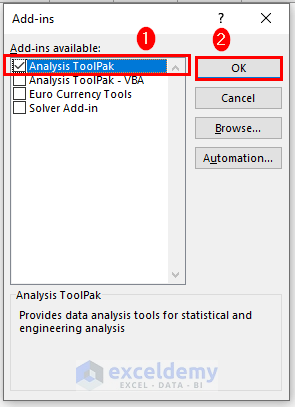
- Let’s do some analysis using this add-in.
Read More: How to Convert Qualitative Data to Quantitative Data in Excel
Descriptive Analysis with the ToolPak
- Select range C5:C14.
- Go to the Data tab and select Data Analysis (This will be available once you activate the Analysis ToolPak add-in).
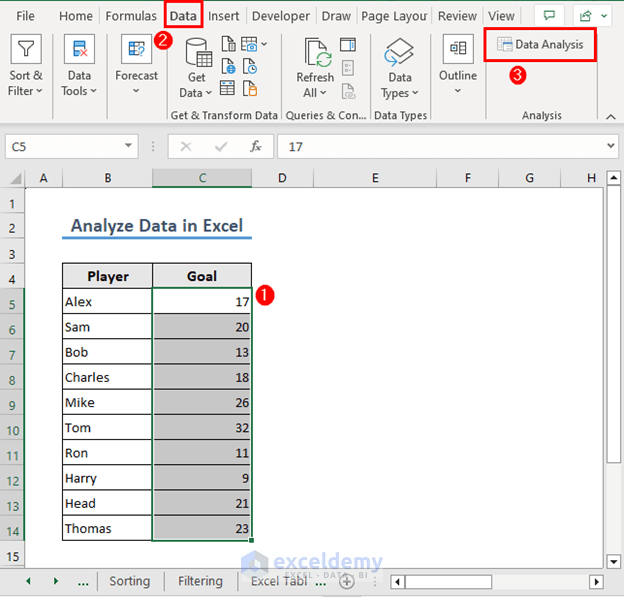
- A Data Analysis box will pop up. Select the Descriptive Statistics option and click OK.
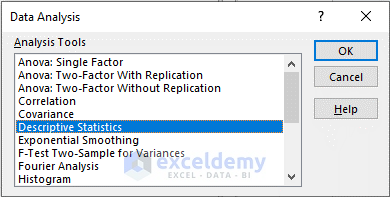
- Set the input range and the output range and click OK. Check Summary statistics.

- You will get the descriptive statistics of the selected input range in your Excel workbook.
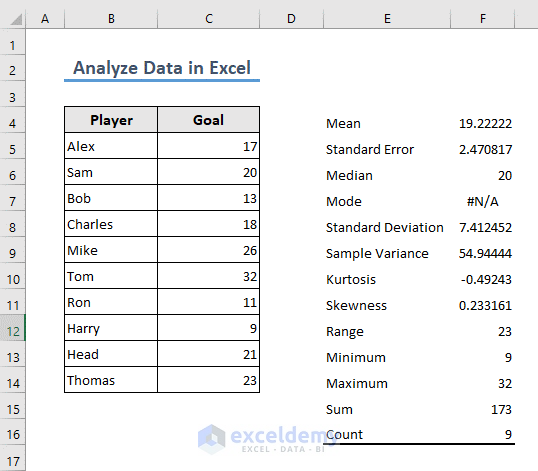
Read More: How to Make Histogram Using Analysis ToolPak
ANOVA Analysis in Excel with ToolPak
ANOVA stands for Analysis of Variance. It is a statistical method used to compare the means of two or more groups to determine if there are any significant differences between them.
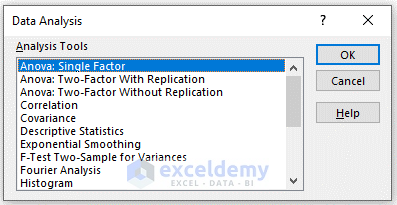
- Go to the Data tab and select Data Analysis.
- Select ANOVA from the Data Analysis box and click on OK.
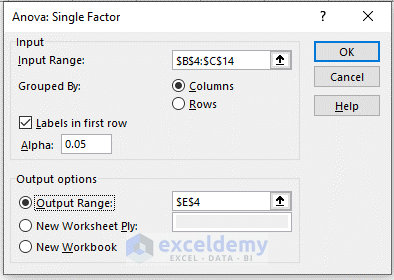
- Set the input and output ranges.
- Excel will perform the analysis for you.
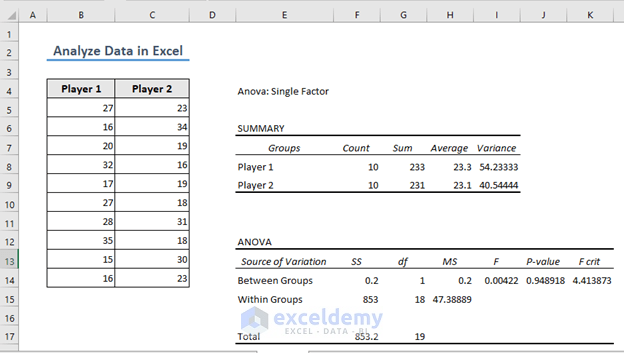
Read More: How to Analyze Data in Excel Using Pivot Tables
Things to Remember
- Data Validation ensures accuracy.
- The INDEX-MATCH function is better than the VLOOKUP function.
- You need to refresh the Pivot Table when you change your dataset.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the advantages of using the Analyze Data feature in Excel over manual analysis techniques?
Advantages of using the Analyze Data feature in Excel over manual analysis techniques include saving time by automating tasks, an easy-to-use interface, lots of helpful tools and functions, the ability to customize, and working well with other Excel features.
2. What is the difference between descriptive and inferential statistics?
Descriptive statistics help describe data by summarizing it while inferential statistics help make predictions about a larger group based on a smaller sample.
3. What are the uses of ANOVA?
ANOVA is used to compare the averages of different groups, see how categorical variables affect outcomes, analyze experiments, and understand different sources of variation in data.
Analyze Data in Excel: Knowledge Hub
- How to Install Data Analysis in Excel
- How to Use Data Analysis Toolpak in Excel
- How to Enter Data for Analysis in Excel
- How to Use Analyze Data in Excel
- [Fixed!] Data Analysis Not Showing in Excel
- How to Analyze Raw Data in Excel
- How to Analyze Large Data Sets in Excel
- How to Analyze Text Data in Excel
- How to Analyze Time Series Data in Excel
- How to Analyze Sales Data in Excel
<< Go Back to Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

