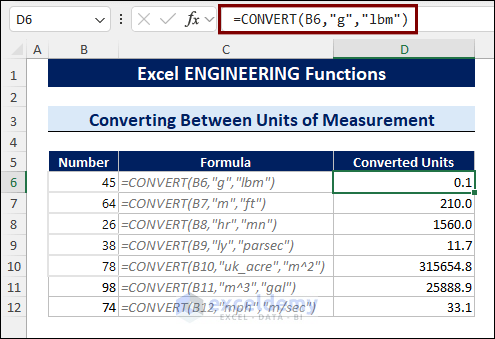
Method 1 – Using the CONVERT Function to Convert Between Units of Measurement
To convert a gram unit into a pound mass unit, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the formula:
=CONVERT(B6,"g","lbm")
B6 is the cell that contains the number value you want to convert.
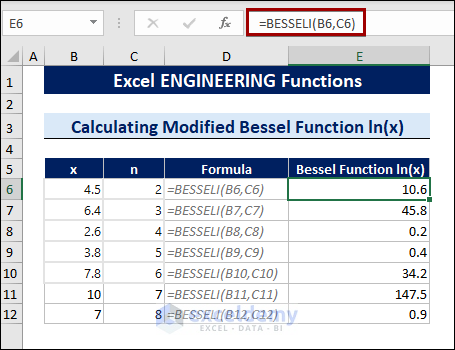
Method 2 – Using Bessel Functions
To calculate the In(x) function, also known as the hyperbolic Bessel function, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=BESSELI(B6,C6)
B6 is the number where the function will be evaluated, and C6 is the order of the function.
To calculate the Jn(x) function, use the following formula:
=BESSELJ(B6,C6)
To calculate the Kn(x) use the following formula:
=BESSELK(B6,C6)
To calculate the Weber function or the Neumann function Yn(x), use the following formula:
=BESSELY(B6,C6)
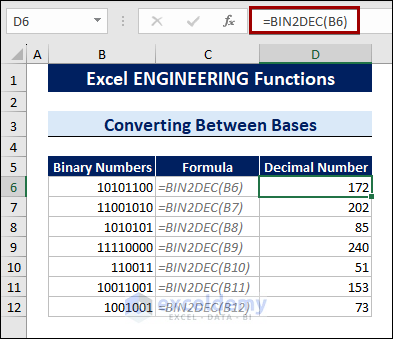
Method 3 – Using Engineering Functions to Convert Numbers Between Bases
3.1 Convert Binary Numbers into Other Bases
The BIN2DEC function is the dedicated Excel function to convert a binary value into a decimal.
To convert binary numbers into decimals, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=BIN2DEC(B6)
Here, B6 is the cell containing the binary number.
To convert the binary numbers into the hexadecimal base, use the following formula:
=BIN2HEX(B6)
To convert the binary numbers into the octal base, use the following formula:
=BIN2OCT(B6)
Note: The number should not exceed 10 characters; otherwise, the #NUM error will appear.
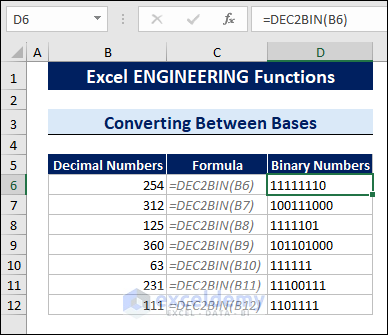
3.2 Convert Decimal Numbers into Other Bases
The DEC2BIN function converts decimal numbers into binary numbers.
To convert decimal numbers into binary numbers, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=DEC2BIN(B6)
B6 is the cell containing the decimal number.
To convert the decimal numbers into the hexadecimal base, use the following formula:
=DEC2HEX(B6)
To convert the decimal numbers into the octal base, use the following formula:
=DEC2OCT(B6)
3.3 Convert Hexadecimal Numbers into Other Bases
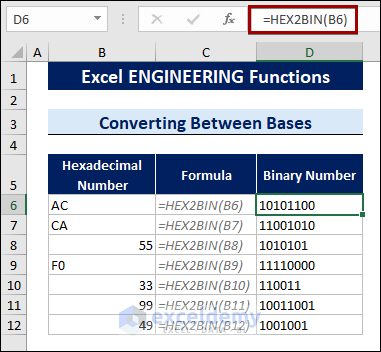
The HEX2BIN function converts hexadecimal numbers into binary numbers.
To convert hexadecimal numbers into binary numbers, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=HEX2BIN(B6)
Here, B6 is the cell containing the hexadecimal number.
To convert the hexadecimal numbers into the decimal numbers, use the following formula:
=HEX2DEC(B6)
To convert the hexadecimal numbers into the octal base, use the following formula:
=HEX2OCT(B6)
3.4 Convert Octal Numbers into Other Bases
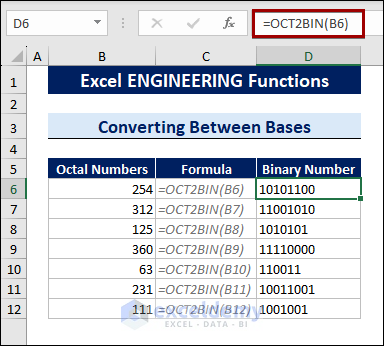
The OCT2BIN function converts octal numbers into binary numbers.
To convert octal numbers into binary numbers, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=OCT2BIN(B6)
B6 is the cell containing the octal number.
To convert the octal numbers into the decimal base, use the following formula:
=OCT2DEC(B6)
To convert the octal numbers into the hexadecimal base, use the following formula:
=OCT2HEX(B6)
Method 4 – Using Engineering Functions to Calculate Error Functions
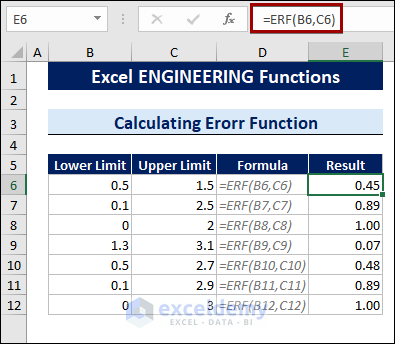
Excel offers the ERF function to calculate the error function between two limits.
To calculate the Error function, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=ERF(B6,C6)
B6 and C6 cells are the upper and lower limits of the Error function.
The ERF.PRECISE function integrates considering one limit to zero(0). This function was introduced in the Excel 2010 version. The ERF function could not take negative values as limits. But in this improved version, it takes negative function arguments.
To calculate the Error function considering the one limit to zero (0), use the following formula:
=ERF.PRECISE(B6)
Calculate the complementary Error function with the ERFC function. It takes the lower limit as an argument, and the upper limit is always infinity.
To calculate the complementary error function between a limit and infinity, use the following formula:
=ERFC(B6)
To calculate the complementary Error function for negative values, use the following formula:
=ERFC.PRECISE(B6)
Method 5 – Using Engineering Functions to Calculate Bitwise Values
To calculate a bitwise ‘And’ of two numbers, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=BITAND(B6,C6)
B6 and C6 are the two decimal values.
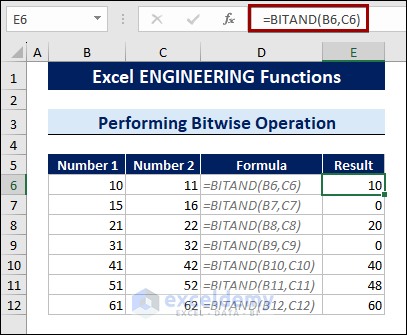
The BITAND function calculates the binary values of 10 (1010) and 11 (1011) at first. Both the digits have 1 in the 2nd and 4th positions from the right. So, the return binary value will be 1010. Converting 1010 into a decimal value returns 10.
To calculate a bitwise ‘Or’ of two numbers, use the following formula:
=BITOR(B6,C6)
To calculate a bitwise ‘Exclusive Or’ of two numbers, use the following formula:
=BITXOR(B6,C6)
To calculate a number shifted left by a specified number of bits, use the following formula:
=BITLSHIFT(B6,C6)
To calculate a number shifted right by a specified number of bits, use the following formula:
=BITRSHIFT(B6,C6)
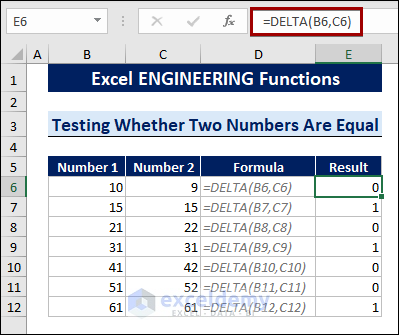
Method 6 – Using the DELTA Function to Test Whether Two Numbers Are Equal
The DELTA function differentiates between two numbers. If the two numbers are equal, it returns 1; otherwise, it returns 0.
To test whether two numbers are equal, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=DELTA(B6,C6)
The cells B6 and C6 are the two numbers.
Method 7 – Using the GESTEP Function to Test Whether a Number Is Greater Than the Other
Test whether one number is greater than another. The GESTEP function tests the two numbers and returns 1 for greater than or equal value, and otherwise returns 0.
To test whether a number is greater than or equal to another, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=GESTEP(B6,C6)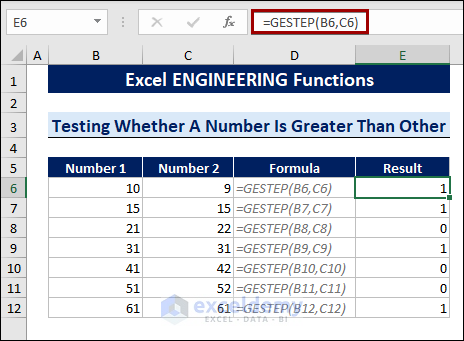
Method 8 – Using Engineering Functions for Complex Numbers
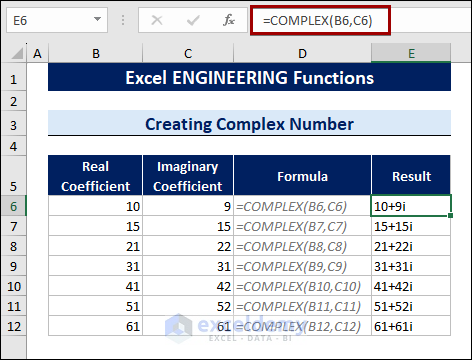
8.1 Creating a Complex Number
The COMPLEX function creates a complex number with the given values of real and imaginary coefficients.
Create a complex number in Excel, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=COMPLEX(B6,C6)
Cells B6 and C6 are the values of real and imaginary coefficients.
Find the only real coefficient of a complex number, use the following formula:
=IMREAL(E6)
Cell E6 contains the complex number and will return the real coefficient 10.
To find the only imaginary coefficient of a complex number, use the following formula with the IMAGINARY function:
=IMAGINARY(E6)
Cell E6 contains the complex number and will return the imaginary coefficient 9.
To find the conjugate complex number, use the following formula:
=IMCONJUGATE(E6)
Cell E6 contains the complex number and will return the conjugate complex number 10-9i.
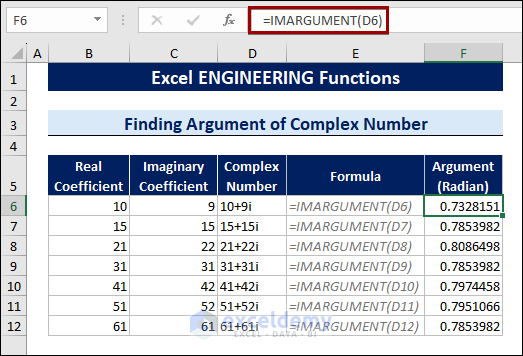
8.2 Finding Modulus and Argument of Complex Number
The IMARGUMENT and the IMABS functions calculate the arguments and the modulus of complex numbers.
To find the argument of a given complex number, follow the procedures below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=IMARGUMENT(D6)
Cell D6 contains the complex number 10+9i.
To calculate the modulus of the complex number, use the following formula:
=IMABS(D6)
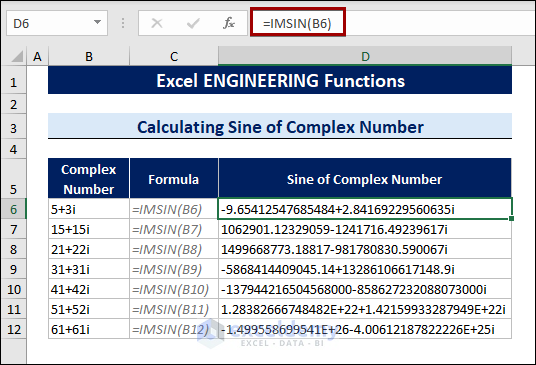
8.3 Calculating Sine Values of Complex Numbers
Calculating the sine values of a complex number is not a big deal. The IMSIN function calculates the sine value and eases the trigonometric operation for complex numbers.
To calculate the sine values, follow the procedures below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=IMSIN(B6)
The B6 cell contains the complex number 5+3i.
To calculate the hyperbolic sine of a complex number, use the following formula:
=IMSINH(B6)
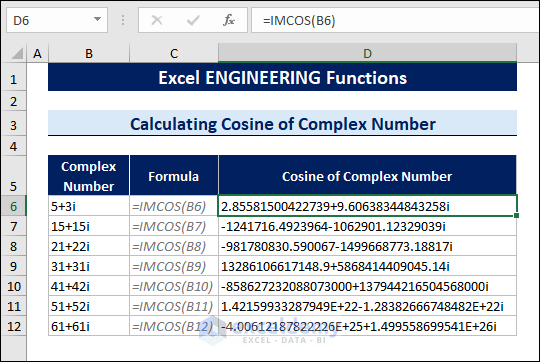
8.4 Calculating Cosine Values of Complex Numbers
The IMCOS function calculates the cosine value of complex numbers.
To calculate the cosine values of complex numbers, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=IMCOS(B6)
The B6 cell contains the complex number.
To calculate the hyperbolic cosine of the complex number, use the following formula:
=IMCOSH(B6)
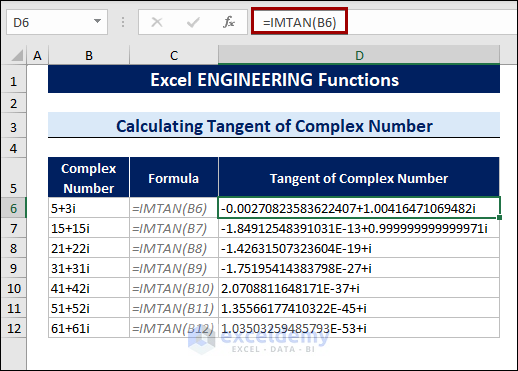
8.5 Calculating Tangent Values of Complex Numbers
The IMTAN function calculates the tangent value of complex numbers.
To calculate the tangent values of complex numbers, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=IMTAN(B6)
The B6 cell contains the complex number.
To calculate the hyperbolic tangent of the complex number, use the following formula:
=IMTANH(B6)
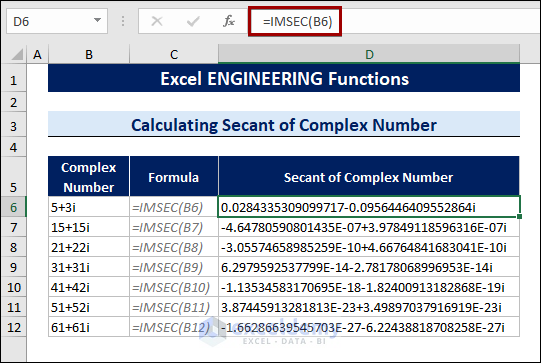
8.6 Calculating Secant Values of Complex Numbers
Excel offers the IMSEC function to find the secant value of complex numbers, in addition to the sine, cosine, and tangent values.
To calculate the secant value, follow the procedures below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=IMSEC(B6)
B6 is the cell that contains the complex number.
To find the hyperbolic secant value of this particular complex number, use the following formula:
=IMSECH(B6)
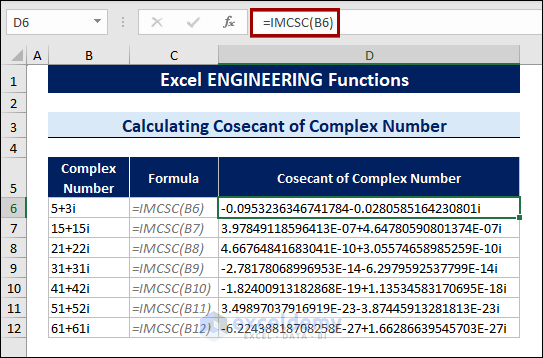
8.7 Calculating Cosecant Values of Complex Numbers
You may also need to find the cosecant values of complex numbers right now. So, you can use the IMCSC function in a similar manner.
To calculate the cosecant values by using the IMCSC function, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=IMCSC(B6)
The B6 cell contains the complex number.
To find the hyperbolic cosecant values by using the IMCSCH function, use the following formula:
=IMCSCH(B6)
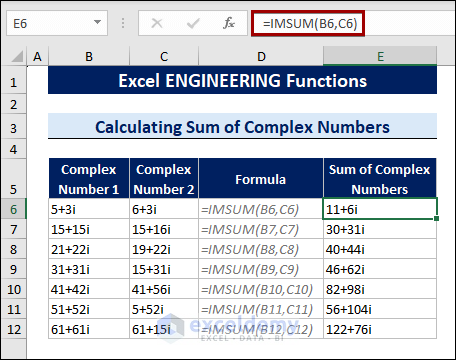
8.8 Calculating Sum and Subtraction of Complex Number
The IMSUM and IMSUB functions calculate the sum and subtraction of two complex numbers.
To calculate the sum of two complex numbers, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=IMSUM(B6,C6)
Cells B6 and C6 contain two complex numbers.
To calculate the subtraction of two complex numbers, use the following formula:
=IMSUB(B6,C6)
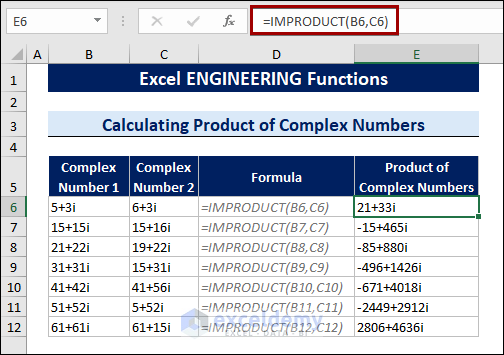
8.8 Calculating Product and Division of Complex Number
The IMPRODUCT and IMDIV functions calculate the product and division of two complex numbers.
To calculate the product of two complex numbers, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=IMPRODUCT(B6,C6)
Cells B6 and C6 contain two complex numbers.
To calculate the division of two complex numbers, use the following formula:
=IMDIV(B6,C6)
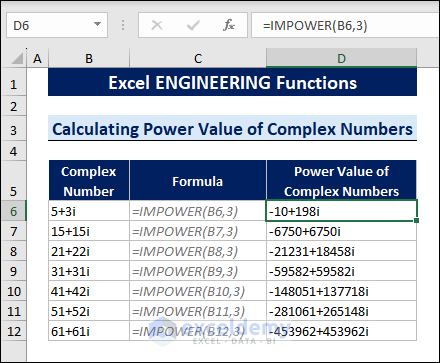
8.9 Calculating the Power Value of Complex Number
The IMPOWER function calculates the power value of any complex number.
To calculate the power value of any complex number, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=IMPOWER(B6,3)
B6 is the cell containing the complex number, and 3 is the power value.
To particularly calculate the square root of a complex number, you can use the IMSQRT function. Use the following formula:
=IMSQRT(B6)
8.10 Calculating Logarithmic Value of Complex Numbers
The IMLN function calculates the natural logarithm of a complex number.
To calculate the natural logarithm of a complex number, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=IMLN(B6)
B6 contains a complex number.
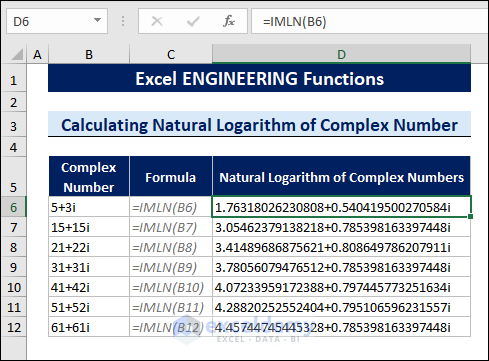
You can also calculate the logarithm value for 2 and 10 bases.
To calculate the 2-base logarithm of a complex number, use the following formula:
=IMLOG2(B6)
To calculate the 10-base logarithm of a complex number, use the following formula:
=IMLOG10(B6)
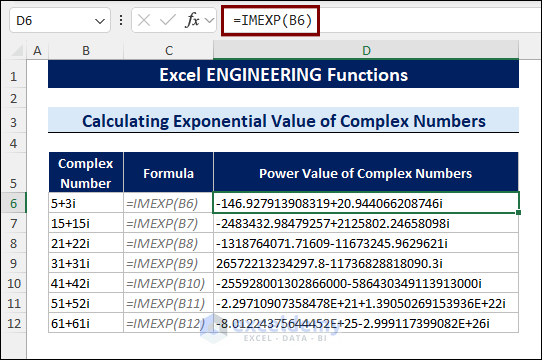
8.11 Calculating Exponential Value of Complex Numbers
The IMEXP function calculates the exponential value of a complex number.
To calculate the exponential value of a complex number, follow the steps below:
- Select a cell.
- Type the following formula:
=IMEXP(B6)
B6 contains a complex number.
Download Practice Workbook
<< Go Back to Excel Function Categories | Excel Functions | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

