Example 1 – Horizontal Balance Sheet
In the Horizontal balance sheet, the Assets and the Liabilities & Equities columns are shown side by side.
Step 1 – Insert the Balance Sheet Headings
- Type in the Balance Sheet header and enter the Date.
- Make two columns for Assets and Liabilities as shown in the example below.
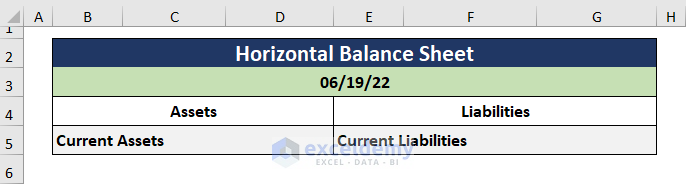
- Enter the types of Assets and Liabilities.
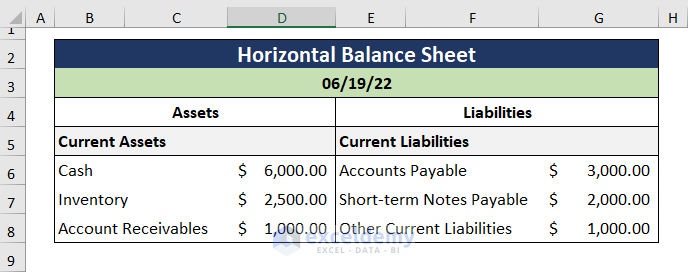
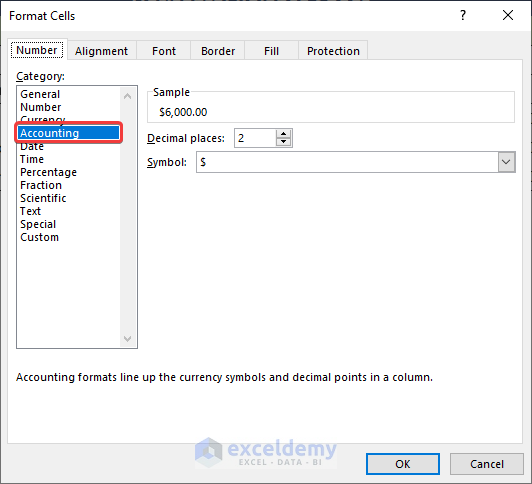
- Open the Format Cells dialog box by pressing Ctrl + 1 and choose Accounting.
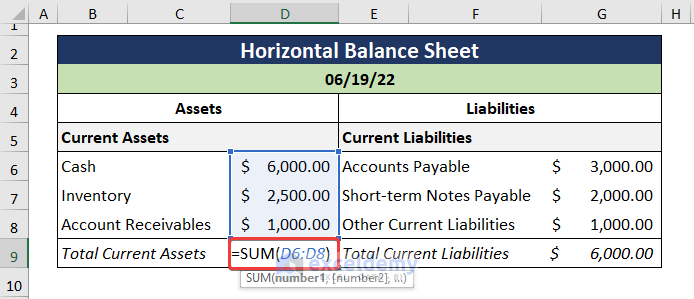
Step 2 – Calculate the Assets, Liabilities, and Equities
- Use the SUM function to compute the sub-total for the Total Current Assets.
=SUM(D6:D8)
The D6:D8 cells refer to the Current Assets.
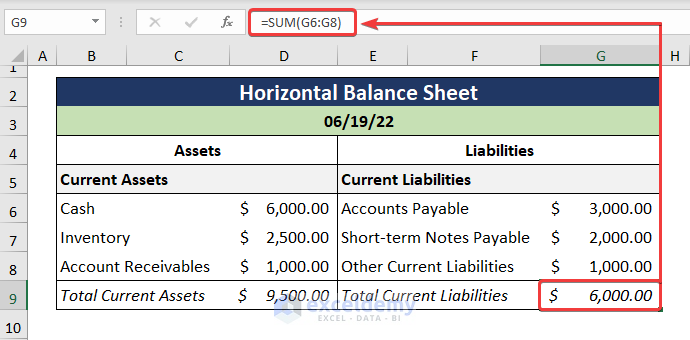
- Calculate the sum for the Total Current Liabilities.
=SUM(G6:G8)
The G6:G8 cells represent the Current Liabilities.
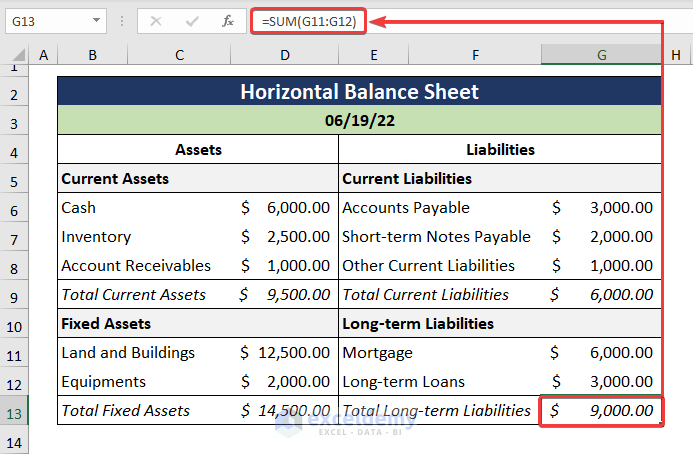
- Add Fixed Assets and calculate the Total Fixed Asset.
=SUM(D11:D12)
Cells D11:D12 consist of the Fixed Assets.

- Calculate the Long-term Liabilities.
=SUM(G11:G12)
The G11:G12 cells represent the Long-term Liabilities.
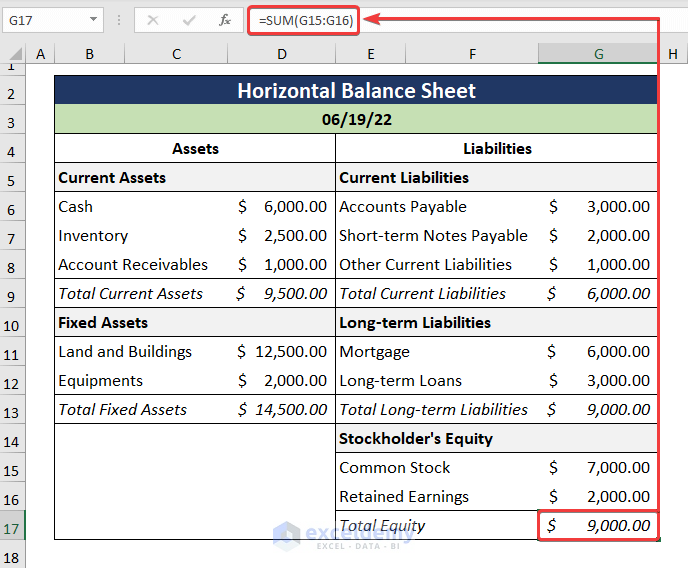
- Include the Stockholder’s Equity in the Liabilities column and compute the Total Equity as illustrated below.
=SUM(G15:G16)
The G15:G16 cells consist of the Stockholder’s Equity.
Step 3 – Calculate the Total Assets and the Liabilities
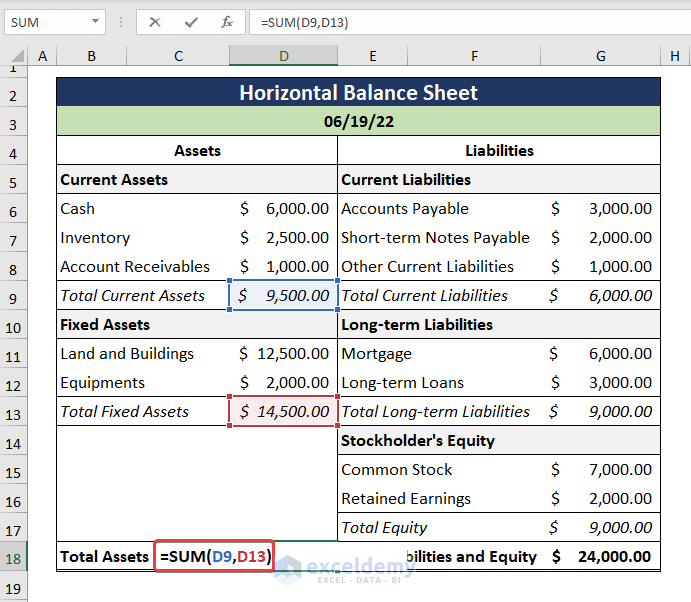
- Get the Total Assets by adding up the Total Current Assets and Total Fixed Assets.
=SUM(D9,D13)
The D9 cell refers to the Total Current Assets while the D13 cell indicates the Total Fixed Assets.
- The Total Liabilities and Equity are obtained with this formula.
=SUM(G9,G13,G17)
In the above expression, the G9 cell points to the Total Current Liabilities, next the G13 cell refers to the Total Long-term Liabilities, and finally, the G17 cell indicates the Total Equity.
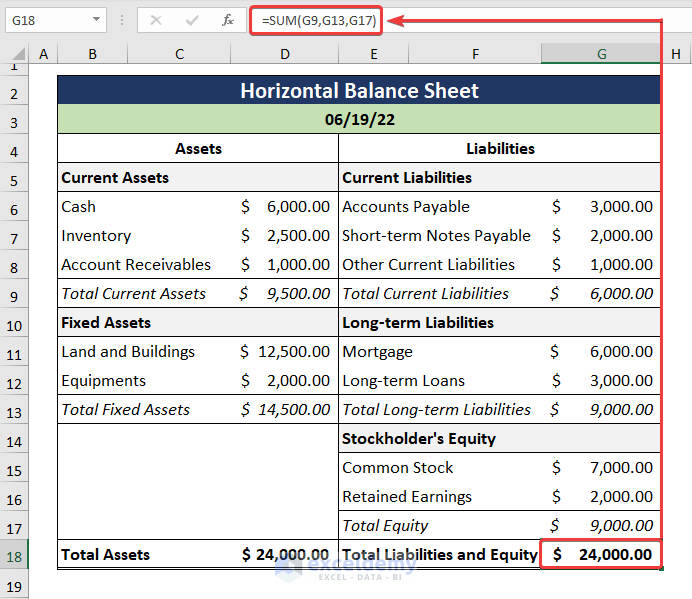
- The values on both the Total Assets and the Total Liabilities and Equity columns must be equal.
Example 2 – Vertical Balance Sheet
A vertical balance sheet consists of two tables one on top of the other. Generally, the Assets column is shown on the top, and the Liabilities and Equities are shown below.
Step 1 – Calculate Total Assets
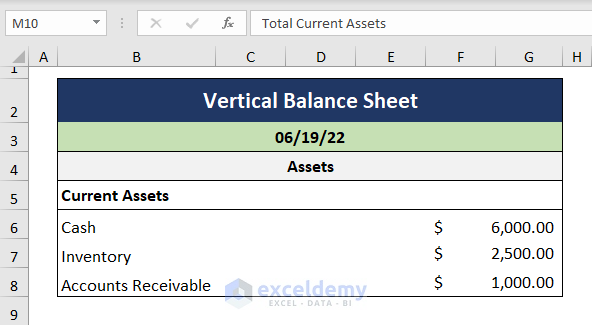
- Make a heading named Assets followed by a sub-heading for Current Assets.
- Enter the Current Asset types on the left side and record the assets’ values on the right side.
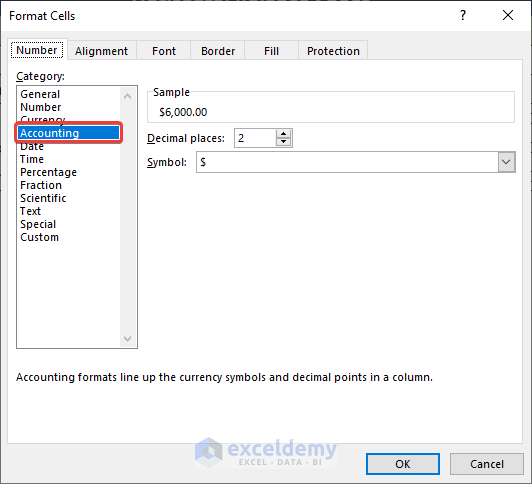
- Press Ctrl + 1 to open the Format Cells dialog box and select Accounting.
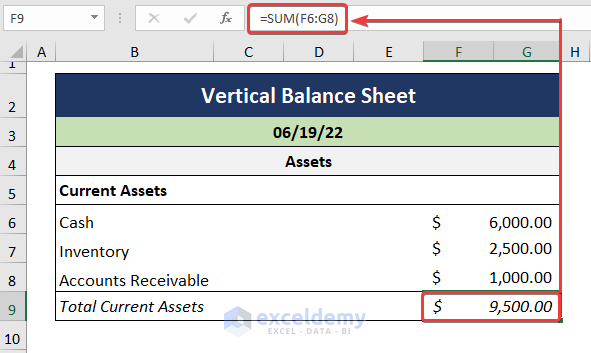
- Compute the Total Current Assets using the SUM function.
=SUM(F6:G8)
In this formula, the F6:G8 cells refer to the types of Current Assets.
- Compute the Total Fixed Assets as shown below.
=SUM(F11:G12)
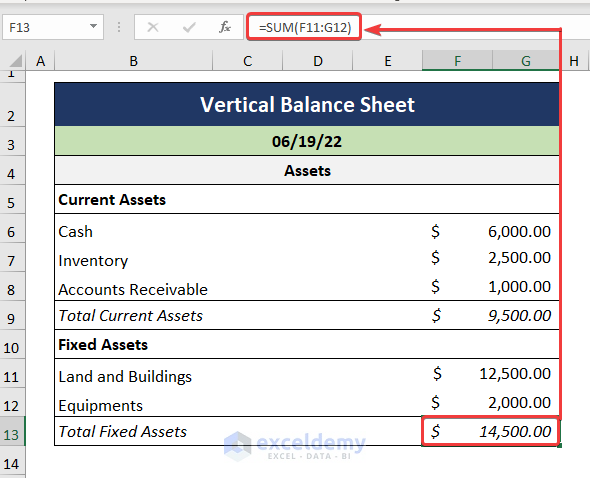
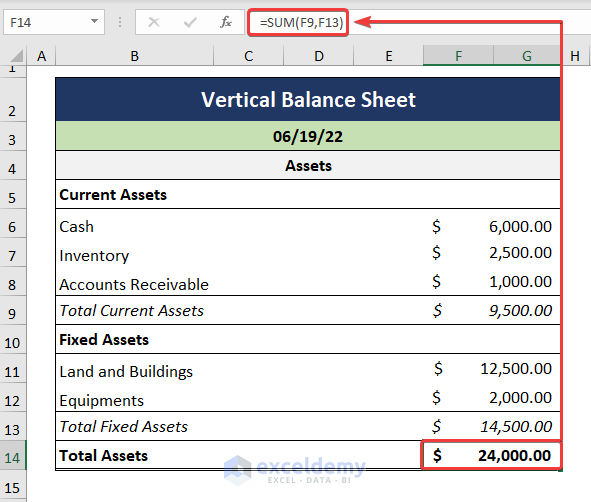
- We get the Total Assets by adding up the Fixed Assets and the Current Assets.
=SUM(F9,F13)
In the above formula, the F9 cell indicates the Total Current Assets, and the F13 cell points to the Total Fixed Assets.
Step 2 – Compute Total Liabilities
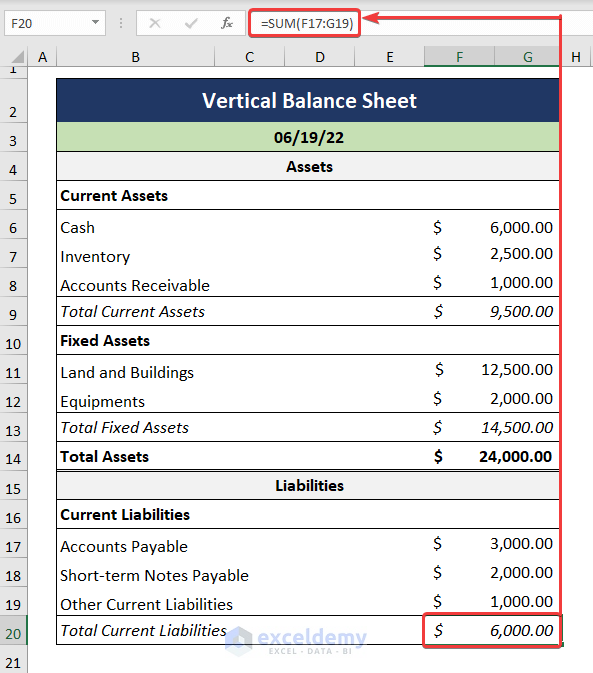
- Enter the types and the corresponding values of the Current Liabilities respectively.
- Calculate the Total Current Liabilities as portrayed below.
=SUM(F17:G19)
- Calculate the Long-term Liabilities as shown below.
=SUM(F22:G23)
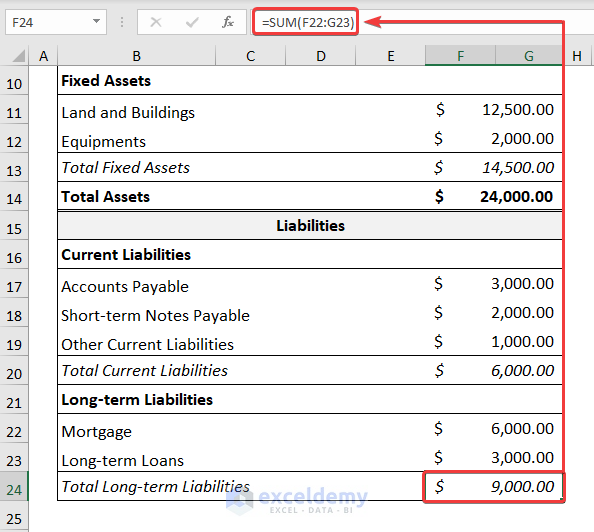
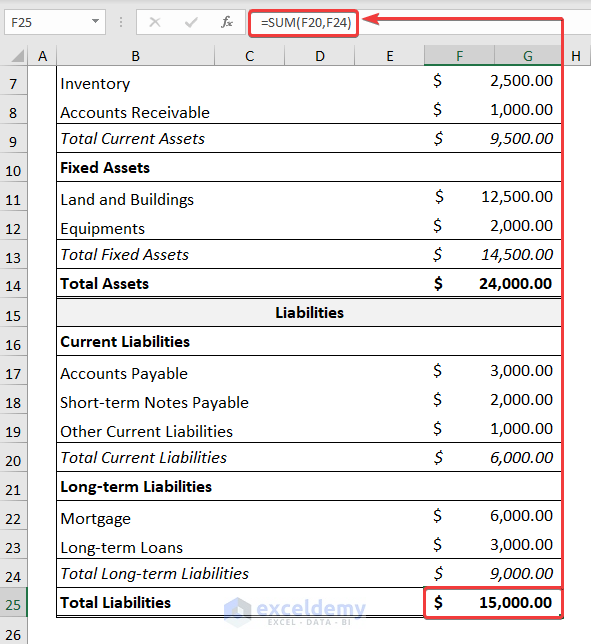
- The Total Liabilities are the sum of Current Liabilities and Long-term Liabilities.
=SUM(F20,F24)
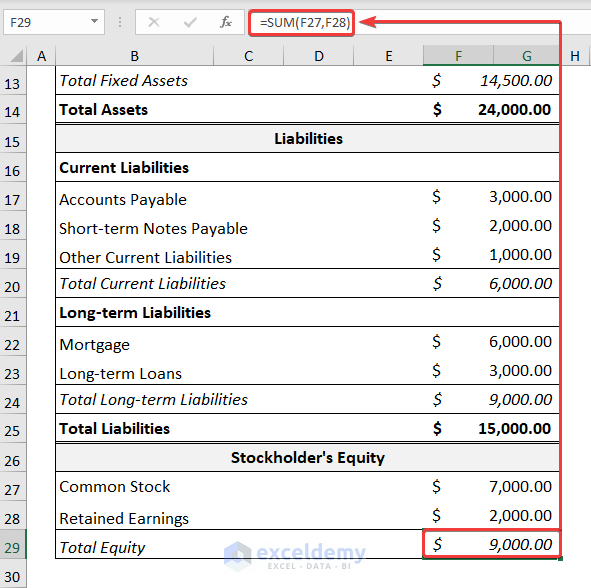
- Obtain the Total Equity using the same process as before.
=SUM(F27,F28)
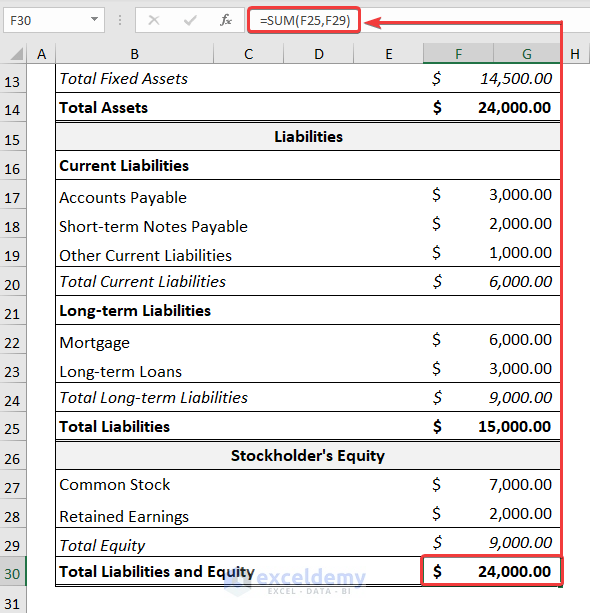
- Obtain the Total Liabilities and Equity.
=SUM(F25,F29)
In the above expression, the F25 cell points to the Total Liabilities, and the F29 cell indicates the Total Equity.
Download the Practice Workbook
How to Make Balance Sheet in Excel: Knowledge Hub
- How to Prepare Balance Sheet from Trial Balance in Excel
- How to Make Stock Balance Sheet in Excel
- How to Make Projected Balance Sheet in Excel
- How to Calculate Running Balance Using Excel Formula
- How to Keep a Running Balance in Excel
- Debit Credit Balance Sheet with Excel Formula
- Calculate Debit Credit Running Balance Using Excel Formula
- How to Make Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet in Excel
- How to Tally a Balance Sheet in Excel
- How to Make Trial Balance in Excel
<< Go Back To Excel For Finance | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

