Method 1 – Using Find and Replace
Step 1: Go to Home Tab > Select Find & Select (in Editing section) > Click on Replace (from the options).
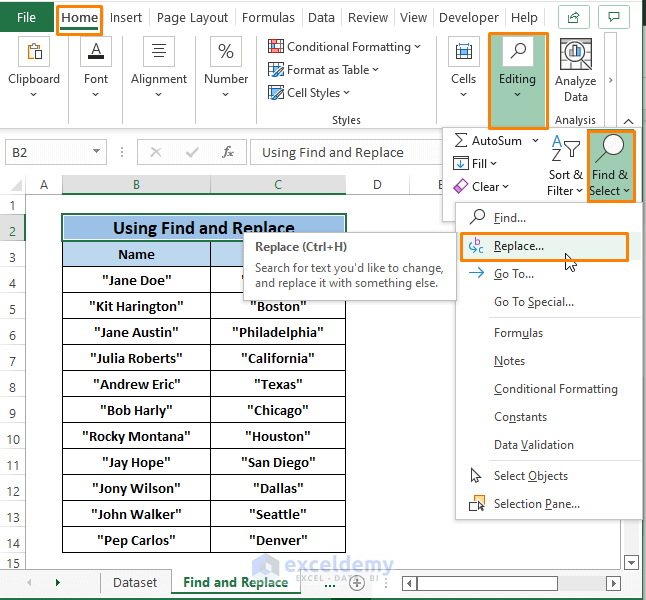
Step 2: The Find and Replace window appears.
In the Find and Replace window,
in Find what command box Insert Quotation Sign (“) and Keep the Replace with command box Empty. Keep other selections Default.
Click on Find All. It’ll show all the entries containing Quotation Signs underneath the Command icons.
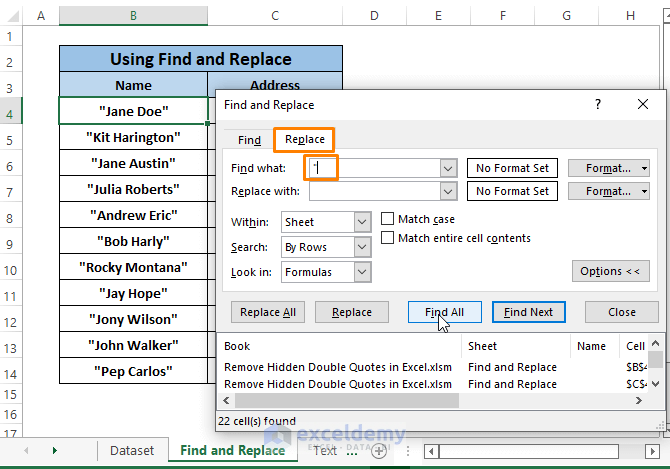
Step 3: Click Replace All.
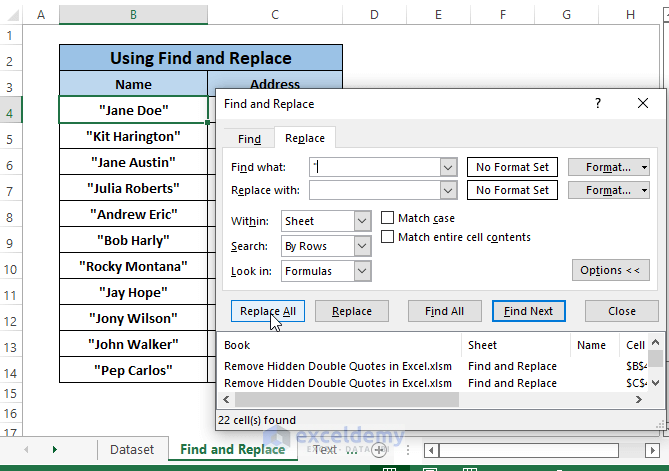
Step 4: A confirmation window opens up saying it has made replacements. Click OK.
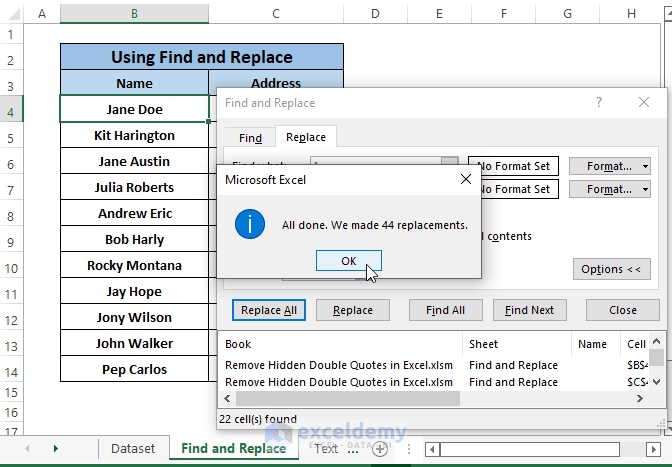
The execution of steps removes all the Double Quotes from the entries. The consequences look like the picture below.
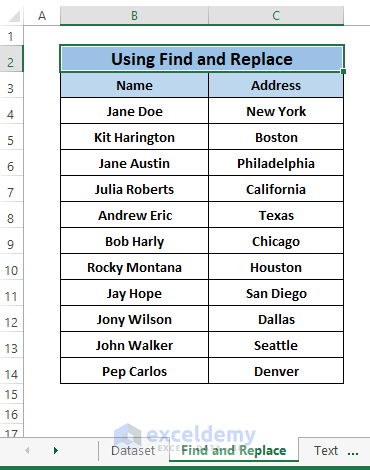
Method 2 – Using Text to Column Function
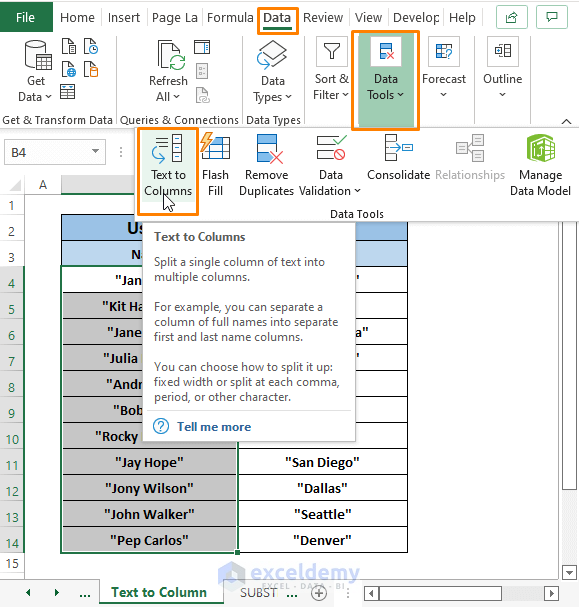
Step 1: Select a range of cells (i.e., Name column). Go to Data Tab > Select Text to Column (in Data Tools section).
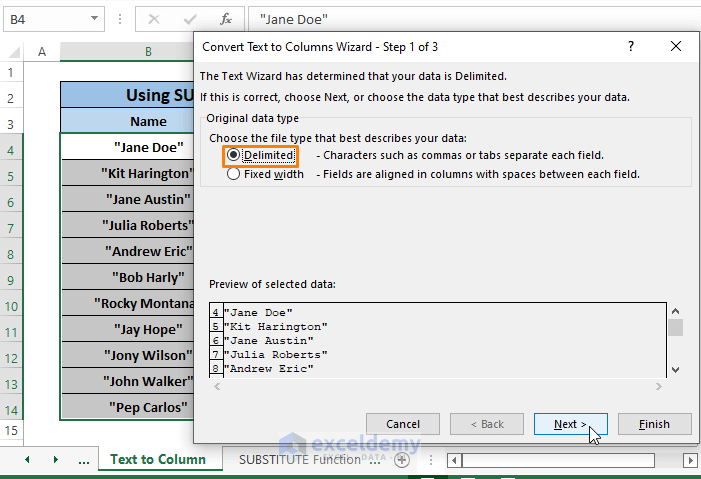
Step 2: Convert text to Columns Wizards Steps 1 of 3 window appears. Choose Delimited as Choose the file type that best describes your data. Click Next.
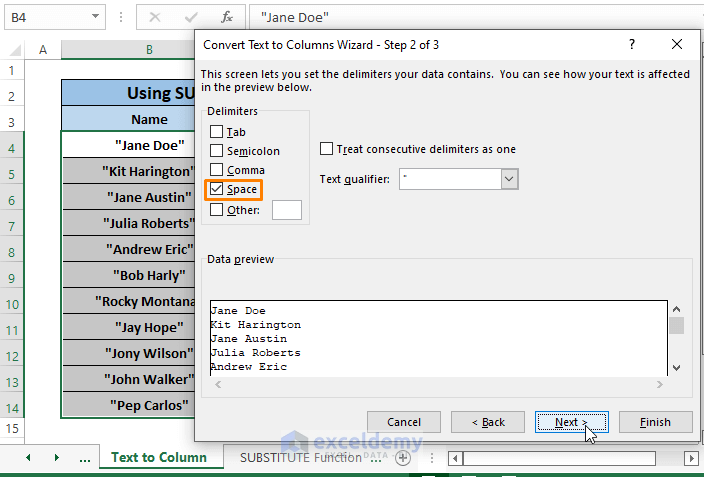
Step 3: In the Convert text to Columns Wizards Steps 2 of 3 window, Checked Space as Delimiters (you can proceed without selecting any delimiter, that will also work). Click Next.
We Unchecked the command box saying as Treat consecutive delimiters as one because we don’t have any consecutive delimiters. Make it Checked if your data type needs to.
Step 4: In the Convert text to Columns Wizards Steps 3 of 3 window, select Column data format as Text. Click Finish.
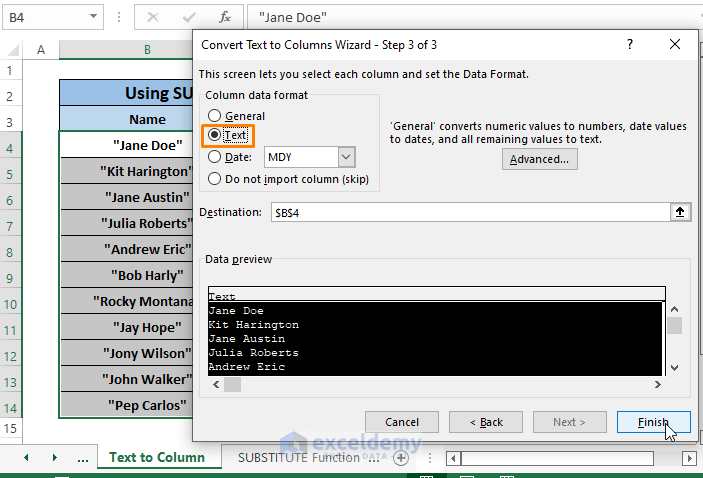
Following all the steps removes Double Quotes from all the selected cells similar to the following image.
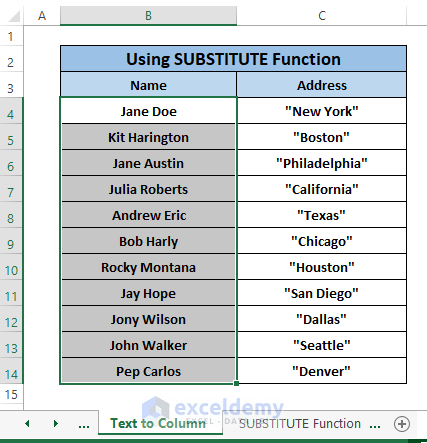
Repeat Steps 1 to 4 for Column C (i.e., Address Column) to come up with a similar result to column B (i.e., Name Column).
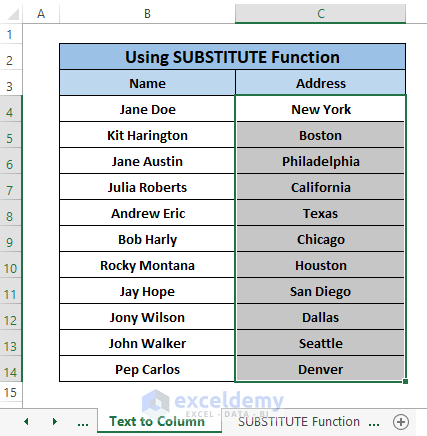
See all the Double Quotes disappear.
Method 3 – Using SUBSTITUTE Function
The SUBSTITUTE function substitutes any characters with declared text in its formula. The syntax of the SUBSTITUTE function is
SUBSTITUTE (text, old_text, new_text, [instance])In the formula,
text; declares the cell reference to change.
old_text; is the text or character to replace within the text.
new_text; is the text to replace with.
[instance]; are the instances the formula replaces old_text with new_text.
Step 1: Paste the following formula in any blank cell (i.e., D4).
=SUBSTITUTE(B4,CHAR(34),"")Here,
B4; is the text.
CHAR(34); is the old_text.
“”; is the new_text.
We keep [instance] as default.
CHAR(34) is the ASCII code for Double Quotation.
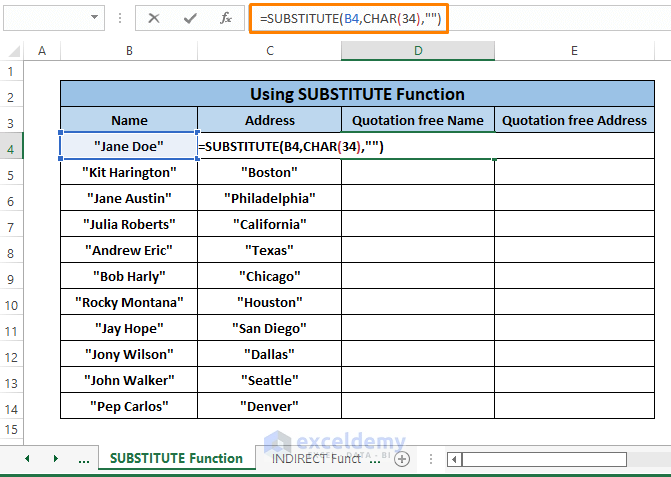
Step 2: Press ENTER and Drag the Fill Handle to bring out all the Names without Double Quotes.
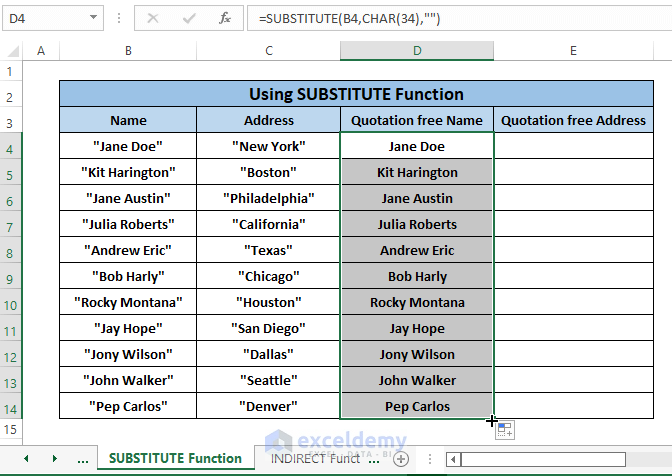
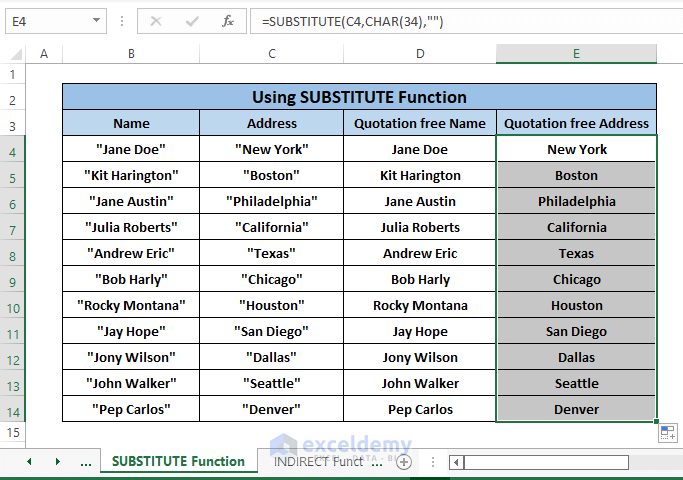
Repeat Steps 1 and 2 for Address column and the consequences will be the same as the following picture.
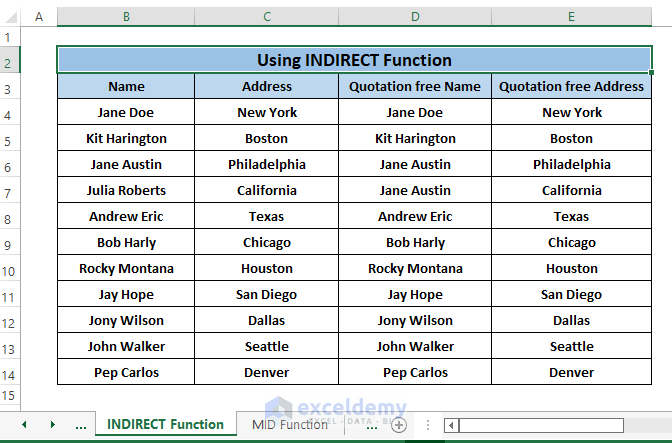
Method 4 – Using INDIRECT Function to Remove Hidden Double Quotes
If we have Double Quotes in formulas not showing in cells. Use the INDIRECT function to remove the quotes. The INDIRECT function has a syntax of.
INDIRECT(ref_text, [a1])Inside the formula,
ref_text; works as cell reference formatted as text.
a1; delivers the logical argument.
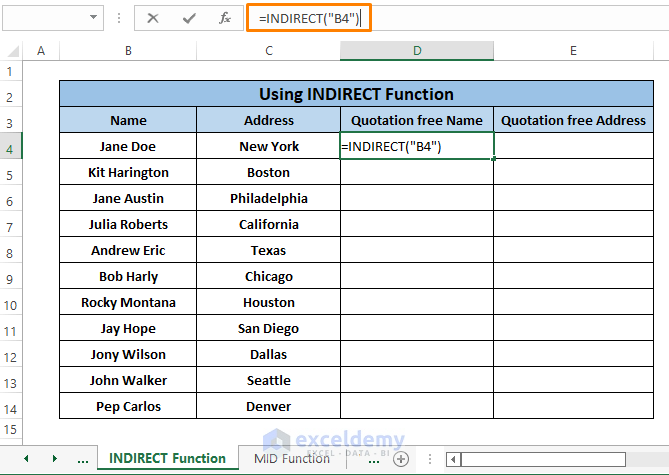
Step 1: Type the following formula in any cells (i.e., D4).
=INDIRECT("B4")Inside the formula,
B4; is the ref_text.
Removing Double Quotes, we don’t need any logical argument(i.e.,a1).
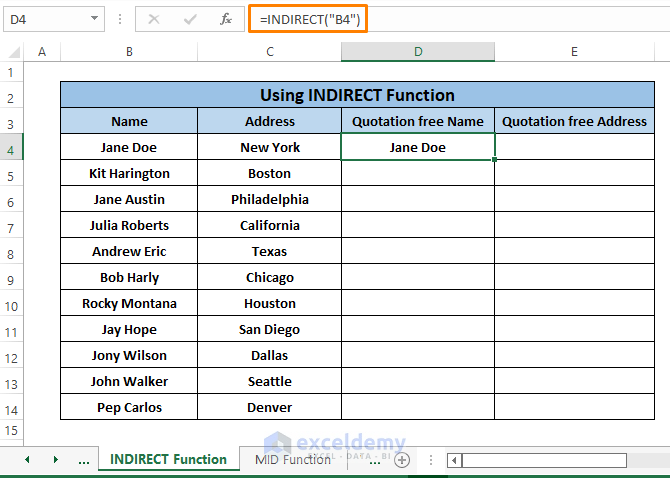
Step 2: Hit ENTER. You’ll get an outcome similar to the image below.
Insert the formula for each cell. It’s a hideous job. if you have a handful of data, you can use it unless I’ll not encourage you to use it.
Follow Steps1 and 2 for each cell then the result will be the same as the image below.
Method 5 – Using MID Function
The MID function fetches characters from the middle of any string. As the Double Quotes are on both sides of any string, we can use the MID function to remove the quotes. The syntax of the MID function is
MID( text, start_position, number_of_characters )Here,
text; is the cell reference you want the characters to extract from.
start_position; is the position within the string you start to extract from.
number_of_characters; is the number of characters from the text you fetch.
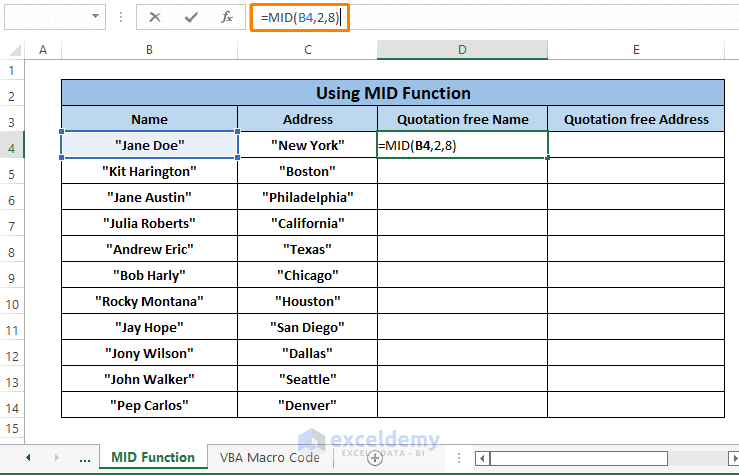
Step 1: Write the following formula in any blank cell (i.e., D4).
=MID(B4,2,8)Here,
B4; is the text.
2; is the start_position, as we want the first character quotation to be removed.
8; is the number_of_characters to extract totally depends on the individual strings.
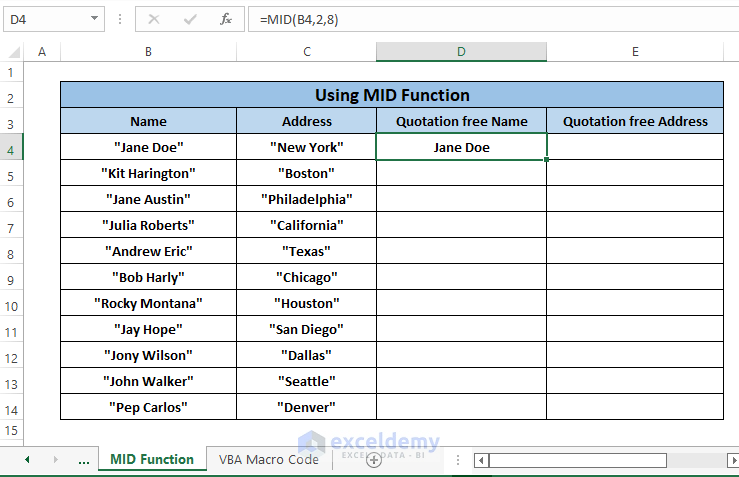
The name “Jane Doe” has a total of 10 characters including the Double Quotes. Fetching characters from character number 2 and then extract a total of 8 characters removing both Quotes on both sides.
Step 2: Press ENTER. The name appears as Double Quotes fewer entries similar to the image below.
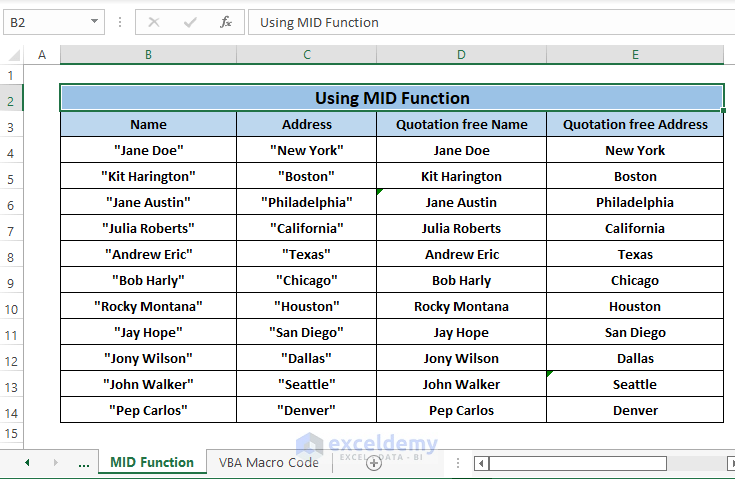
Insert different number_of_characters depending on individual character length. Insert the different number_of_characters for each cell pressing ENTER, you’ll get a depiction like the following picture.
Method 6 – Using VBA Macro Code to Remove Hidden Double Quotes
VBA Macro Code is a very effective tool to achieve a result with less effort. In this case, we can use a couple of lines of VBA Macro Code to remove Double Quotes from any selection.
Step 1: Select a range of cells you want to remove the Double Quotes from.
Step 2: Press ALT+F11 altogether to open Microsoft Visual Basic. In the Microsoft Visual Basic window, from the Toolbar, Click on Insert > Select Module.
Step 3: In the Module, Paste the following Macro Code.
Sub RemoveDoubleQuotes()
Dim c As Range
For Each c In Selection
c.Value = Replace(c.Value, Chr(34), " ")
Next c
End Sub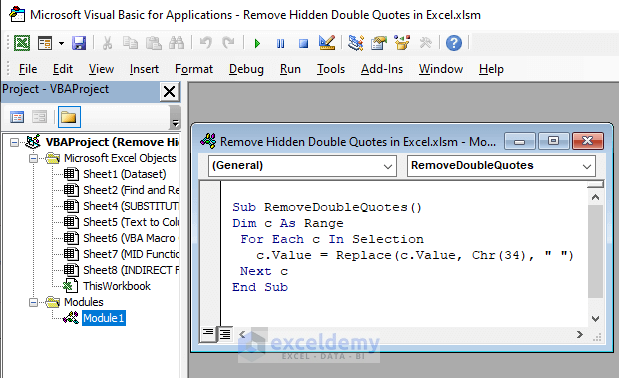
Using the code we apply the formula c.Value to the selection of the worksheet to Replace all the Char(34) (i.e., Double Quotes).
Step 4: Press F5 to run the Macro Code. Back to the worksheet, you’ll see all the double quotes from the entries are removed.
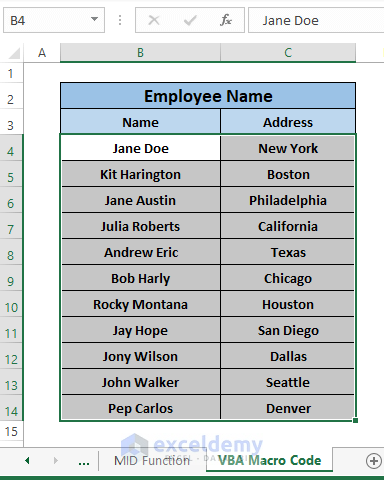
Dataset for Download
Related Articles
- How to Add Single Quotes in Excel
- How to Add Single Quotes and Comma in Excel Formula
- How to Add Single Quotes in Excel for Numbers
- How to Concatenate Single Quotes in Excel
- How to Add Double Quotes in Excel
- How to Add Double Quotes and Comma in Excel with CONCATENATE
- How to Add Double Quotes in Excel Concatenate
<< Go Back to Quotes in Excel | Concatenate Excel | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

