Sometimes, when working with large datasets, Excel won’t compute all the formulas in the cells. One solution to this problem is to use VBA to recalculate everything. In this article, we will show how to use Excel VBA to calculate the Active Sheet.
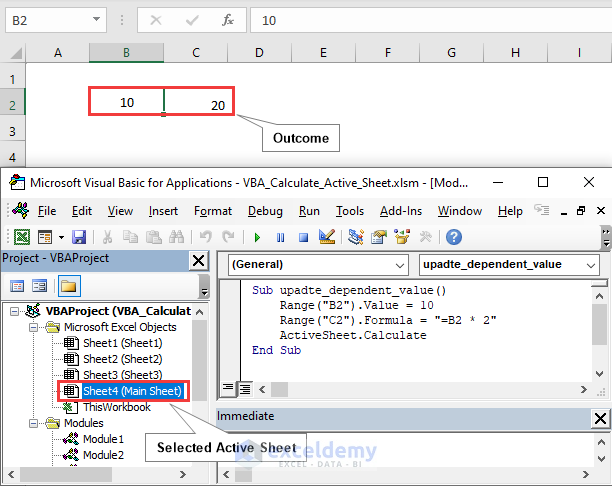
In the above image, we input a value in cell B2 and inserted a formula in cell C2. Using the ActiveSheet.Calculate method, we obtain the outcomes 10 and 20 in cells B2 and C2 respectively.
What Is VBA Calculate Active Sheet?
The Calculate method in VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) is used to recalculate formulas in a worksheet or a particular range of cells. All the formulas in the active worksheet are calculated when applying the ActiveSheet object’s Calculate function.
Code
Sub Calculate_ActiveSheet()
ActiveSheet.Calculate
End SubAfter defining ActiveSheet.Calculate, this subroutine will compute all the formulas on the current sheet and update the values to correspond with any modifications to the referenced cells when executed.
If you need it, follow this link to learn some different ways to write VBA code in Excel.
Calculate the Active Sheet with Excel VBA: 6 Practical Applications
We will now discuss 6 practical applications using the ActiveSheet.Calculate method in VBA to perform calculations in an active sheet. We’ll use a dataset from a workbook containing 4 worksheets to illustrate our methods.
Method 1 – Calculating a Single Sheet
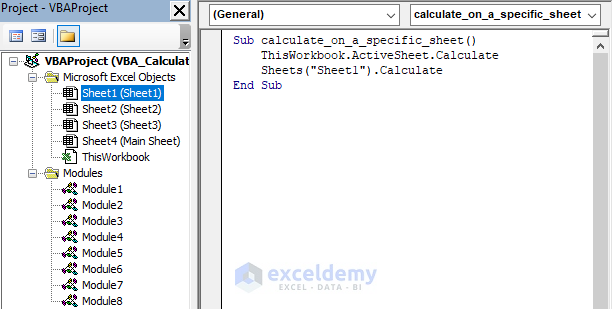
Here, using the Activesheet.Calculate method, all the formulas in the selected active sheet (Sheet1) will be recalculated when we execute the VBA code.
Code
Sub calculate_on_a_specific_sheet()
ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet.Calculate
Sheets("Sheet1").Calculate
End SubMethod 2 – Inserting a Value Using ActiveSheet.Calculate
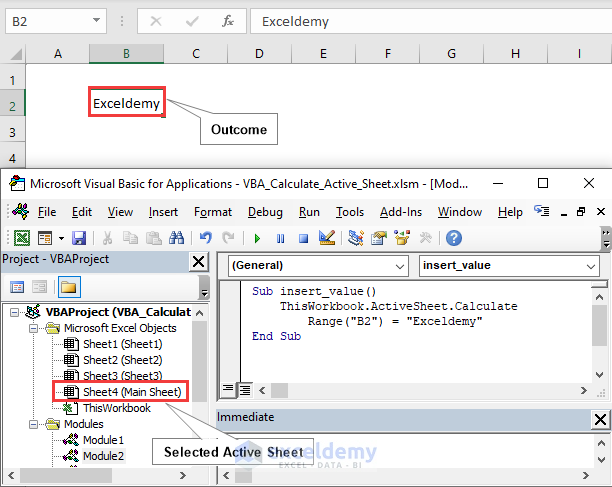
In this case, we select a specific sheet (Main Sheet) and insert the string value “Exceldemy” in cell B2.
Code
Sub insert_value()
ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet.Calculate
Range("B2") = "Exceldemy"
End SubMethod 3 – Updating Dependent Values
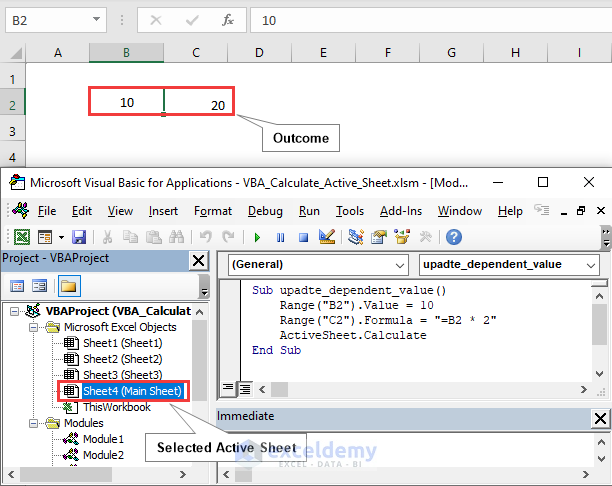
Here, we Insert a value and formula depending on that value, obtaining 20 and 30 in the two consecutive cells B2 and C2.
Code
Sub update_dependent_value()
Range("B2").Value = 10
Range("C2").Formula = "=B2 * 2"
ActiveSheet.Calculate
End SubMethod 4 – Calculating with Conditions
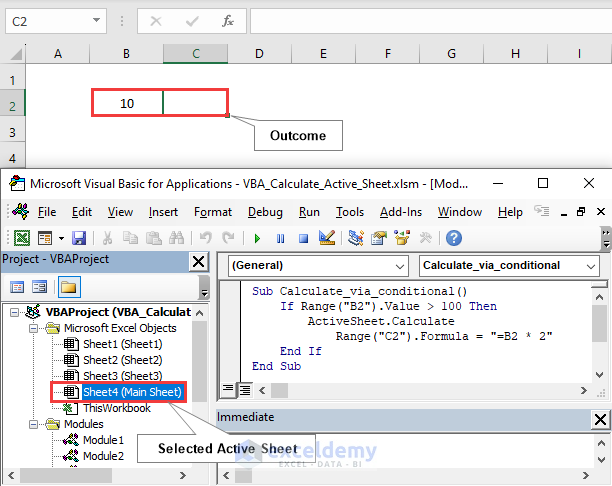
Calculations based on logical expression will also be executable when we use the ActiveSheet.Calculate method. Here we consider logic for whether the value of B2 is greater than 100. B2 = 10, so cell C2 remains blank after executing the VBA code.
Code
Sub Calculate_via_conditional()
If Range("B2").Value > 100 Then
ActiveSheet.Calculate
Range("C2").Formula = "=B2 * 2"
End If
End SubMethod 5 – Finding the Total Number of Rows
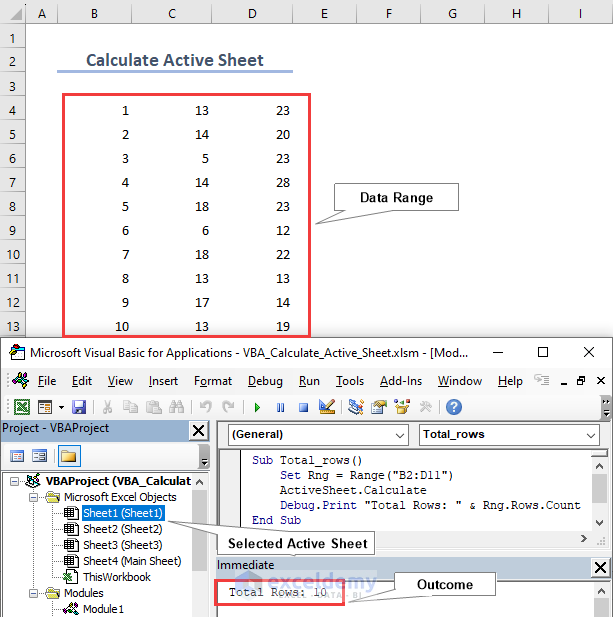
Here we calculate the total number of rows in a range. We select Sheet1, define Rng as a Range (“B2:D11“), and using the Rng.Rows.Count function we obtain Total Rows of 10 in the Immediate window.
Code
Sub Total_rows()
Set Rng = Range("B2:D11")
ActiveSheet.Calculate
Debug.Print "Total Rows: " & Rng.Rows.Count
End SubMethod 6 – Finding the Total Number of Columns
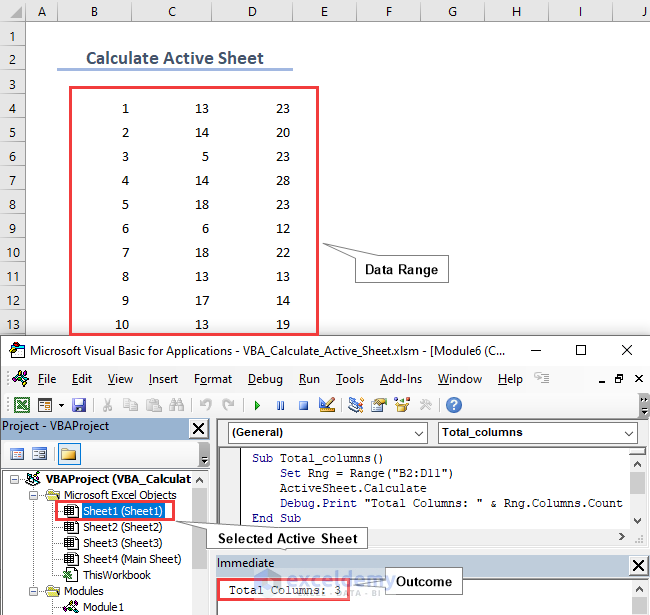
In the same way as counting rows in a range, we can calculate the total number of columns. We select Sheet1, define Rng as a Range (“B2:D11“), and using the Rng.Columns.Count function we obtain Total Columns of 3 in the Immediate window.
Code
Sub Total_columns()
Set Rng = Range("B2:D11")
ActiveSheet.Calculate
Debug.Print "Total Columns: " & Rng.Columns.Count
End SubExcel VBA Manual Calculation on One Sheet Only
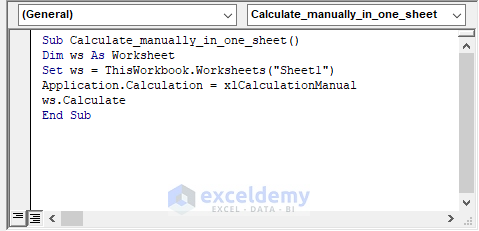
Generally, automatic calculation is the default setting when working with formulas in worksheets. To perform a single, manual calculation, we’ll therefore need to turn off automatic calculation.
First, we declare ws as a worksheet and assign to it Sheet1. Using the Application.Calculation= xlCalculationManual statement we turn off automatic calculation. Finally, ws.Calculate recalculates the formulas in Sheet1.
Code
Sub Calculate_manually_in_one_sheet()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1")
Application.Calculation = xlCalculationManual
ws.Calculate
End SubFrequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
1. How do you calculate active worksheets?
Utilizing the ActiveSheet.Calculate method, we can select active worksheets and calculate accordingly in them. For example, the following lines insert the text ‘Exceldemy ” in cell B2.
ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet.Calculate
Range("B2") = "Exceldemy"2. How do I select an active workbook in Excel VBA?
Use the ActiveSheet.Calculate method in the code and select the required sheet before hitting the Run icon.
Range("B2").Value = 10
ActiveSheet.CalculateThis code inserts 10 in cell B2 of the active workbook.
3. What is the difference between Active Sheet and Selected Sheets in VBA?
One or more worksheets that were specifically chosen within an Excel window are referred to as the Selected Worksheets. There is a specific collection of Selected Worksheets for each Workbook. The worksheet you are observing and working on right now is called the Active Worksheet.
Download Practice Workbook


