Method 1 – Declare Global Variable and Assign Value in VBA
There are numerous advantages to using Global variables. We will address the issues regarding the use of variables and their remedy step by step.
Procedure Level Variable
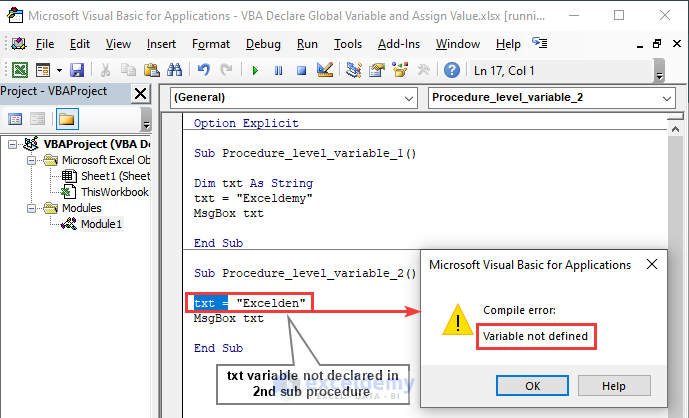
We declared variable typing veteran Dim in the 1st sub-procedure of Module 1. The declaration of that variable didn’t work for the 2nd sub-procedure of the same module; it shows Compile error: Variable not defined.
Module Level Variable
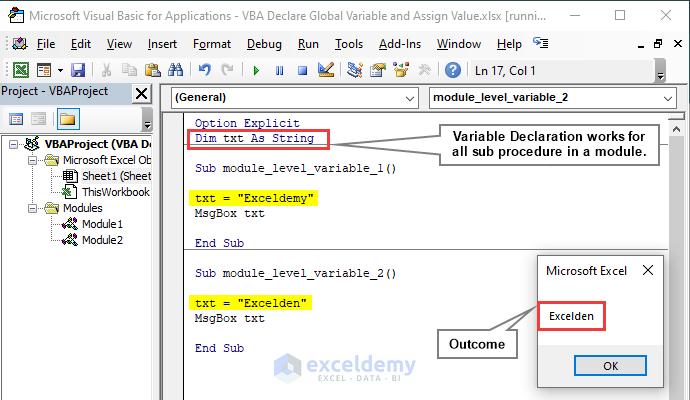
Using veteran Dim, you can declare a variable under the Option Explicit statement representing the module-level variable. A module-level variable allows the execution of all the sub-procedures of a single module.
We obtained Excelden once we run the VBA code of the 2nd sub-procedure.
Global Level Variable
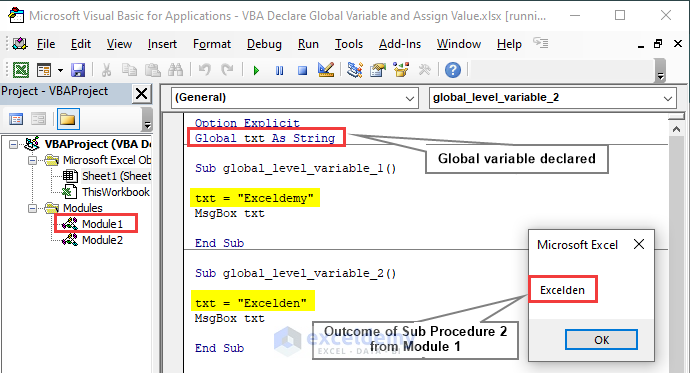
If we want to use a variable that works for all the modules of a workbook, we must write Global or Public instead of widely used Dim under the Option Explicit statement. Get Excelden once we run the VBA code of the 2nd sub-procedure of Module 1. We don’t need to type Dim separately in a separate sub-procedure.
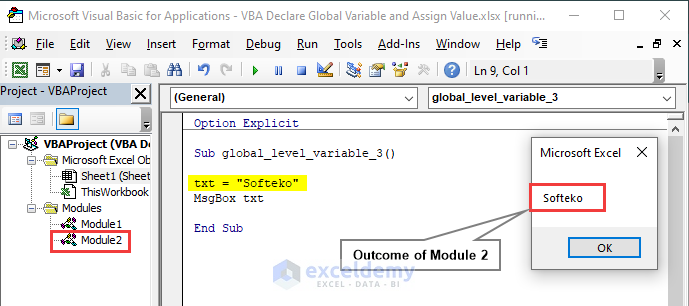
We execute a new code in Module 2 where we didn’t declare the variable in the sub-procedure. The VBA code works and outputs Softeko because we declared txt as a Global variable that works for all the modules in a workbook.
Method 2 – Declare Public Variable in VBA and Assign Value from Excel Cell
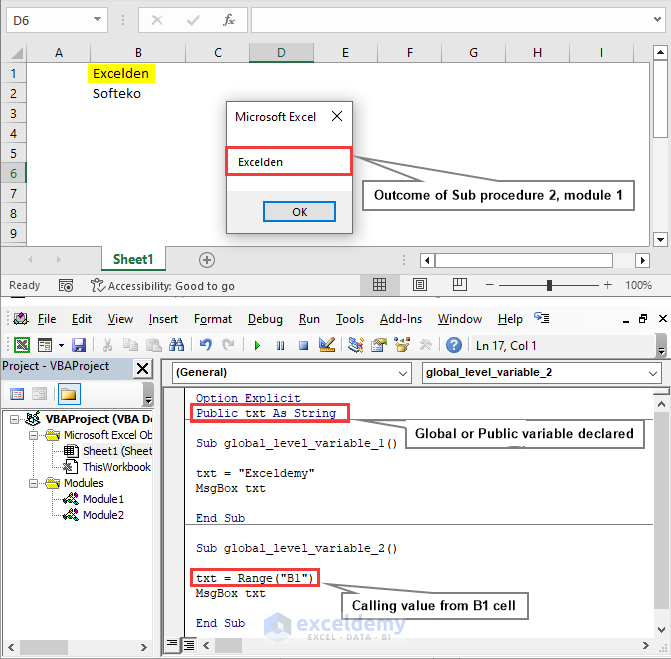
While declaring global or public variables, not only assigning values but also calling from an Excel cell can be done. By calling a value from the B1 cell and executing the VBA code of the 2nd sub-procedure of Module 1, we achieve Excelden in a pop-up message box.
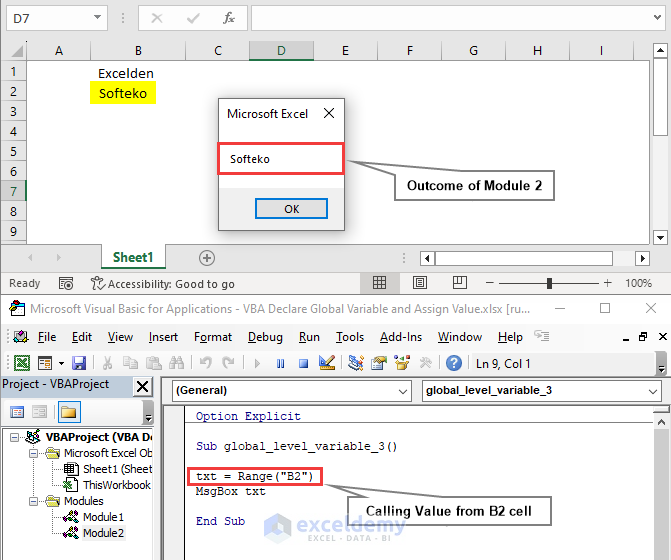
By calling the value from the B2 cell and executing the VBA code of Module 2, we obtain Softeko through a pop-up message box.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
1. Where do I declare global variables in VBA?
Using the keyword Public or Global instead of Dim under the Options explicit statement, we can declare the global level variable. It is usable in any sub-procedure, module, or function in a workbook.
Example: Global a As Integer
2. How is a value assigned to a global variable?
You can define any type of variable such as integer, string, date, decimal, etc. by assigning value in VBA code or calling from an Excel cell while using global-level variables.
For instance, Global a as String, thus we obtain string value for a.
3. How do I assign a cell value to a Variable in VBA?
By referencing a cell from an Excel cell while declaring Global or Public variables, we can assign a cell value. Let’s say, A1= Apple. Writing txt=Range(“A1”) and msgbox txt declaring the txt variable as global, we obtain Apple in a message pop-up box.
Important Notes
- The value of a global or Public variable remains the same throughout all the Sub-procedure, Modules, functions, etc. once the Excel VBA Macro has executed with it.
- In order to define global variables in VBA and have all the variables, it is preferable to maintain a specific module.
- The VBA macro code can only be reset by hitting the stop button, which is the only means to reset the value of the variables.
Takeaways from This Article
- Difference among Procedure level, Module level, and Global level variables.
- Importance and Usability of Global level variable.
- Declaration approaches of Global variables.
- Assigning values through input in VBA code or calling from an Excel cell.
Download Practice Workbook
To practice, please download the Excel Workbook file from the link below.
Related Articles
- Excel VBA: Set Variable to a Cell Value
- Excel VBA Declare Global Variable
- [Fixed!] Excel VBA: Global Variable Loses Value


