Download the Workbook
How to Find and Replace Using VBA – 11 Ways
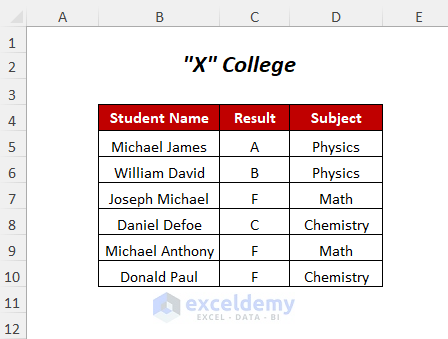
We will use the following table which has the records of test results of some students
Method 1 – Finding a String Without an Optional Parameter
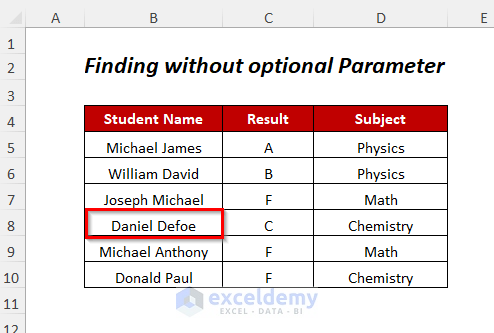
We will find the student’s name marked by a red box, Daniel Defoe, in the Student Name column.
Steps:
- Go to the Developer tab and select the Visual Basic option.
- The Visual Basic Editor will open up.
- Go to Insert and select Module.
- A Module will be created.
- Insert the following code:
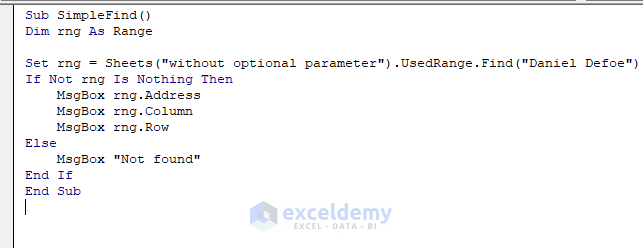
Sub SimpleFind()
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Sheets("without optional parameter").UsedRange.Find("Daniel Defoe")
If Not rng Is Nothing Then
MsgBox rng.Address
MsgBox rng.Column
MsgBox rng.Row
Else
MsgBox "Not found"
End If
End SubHere, rng is declared as a range object, and “without optional parameter” is the name of the sheet.
After finding “Daniel Defoe” in the data range it will return the cell address, column number, and row number of this string in the Message Box.
In case the string is not matched up in the data range, then it will return “Not found”.
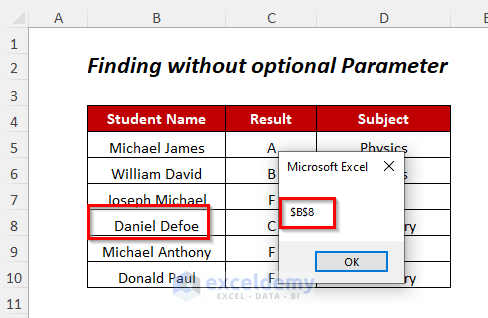
- Press F5.
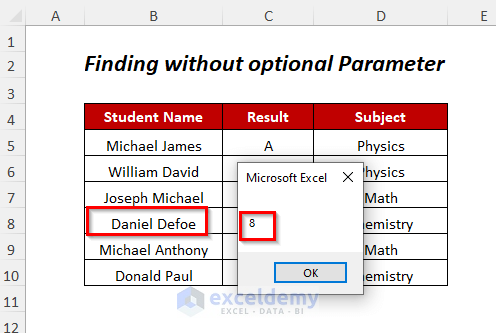
- You will get the following Message Box containing the cell position of the student.
- Press OK.
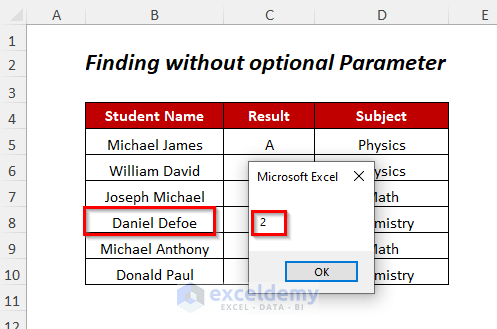
- You will get the column position of this student.
- Press OK.
- Finally, you will get the row position of this student’s name.
Method 2 – Finding Multiple Values With the After Parameter
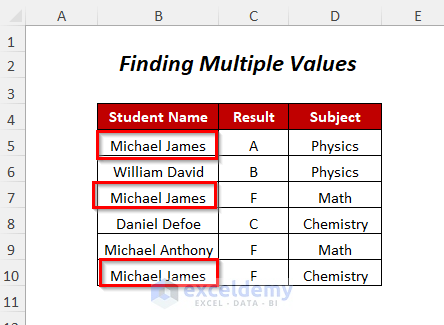
Let’s find all the positions of the student Michael James, which is available multiple times in the dataset.
Steps
- Open a new VBA Module (see the previous Method for exact steps).
- Insert the following code:
Sub findingmultiplevalues()
Dim rng As Range, rng1 As Range, str As String
Set rng = Sheets("multiple values").UsedRange.Find("Michael James")
If rng Is Nothing Then Exit Sub
MsgBox rng.Address
Set rng1 = rng
str = str & "|" & rng.Address
Do
Set rng = Sheets("multiple values").UsedRange.Find("Michael James", After:=Range(rng1.Address))
If InStr(str, rng.Address) Then Exit Do
MsgBox rng.Address
str = str & "|" & rng.Address
Set rng1 = rng
Loop
End SubHere, rng and rng1 are declared as range objects and str as a string variable to store the address of the searched item.
“multiple values” is the sheet name and “Michael James” is the string that is to be found.
str = str & “|” & rng.The address will add the address to the string with a delimiter “|”.
The DO loop will continue through the range to look for other instances and if the address is found for any instances then the loop will end.

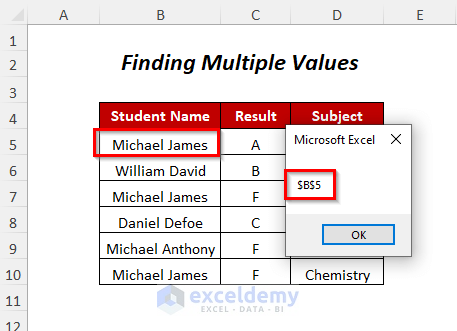
- Press F5.
- You will get the following Message Box containing the first cell position.
- Press OK.
- If it exists, you will get the second cell position of this student.
- Press OK.
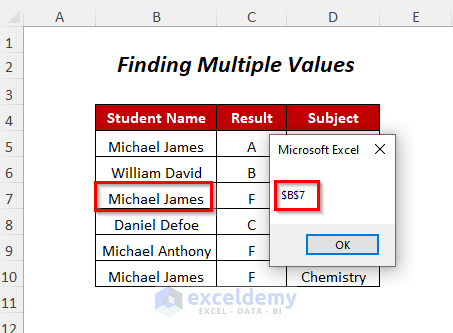
- This will continue for all repetitions of the located string.
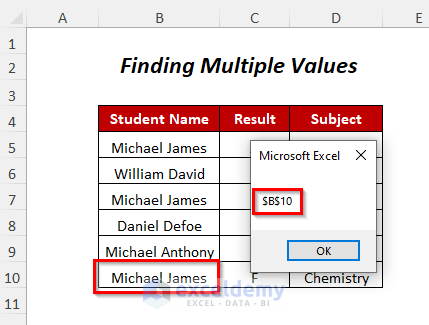
Method 3 – Finding a String With the LookIn Parameter
You can use the LookIn parameter in the VBA code to find your desired string.
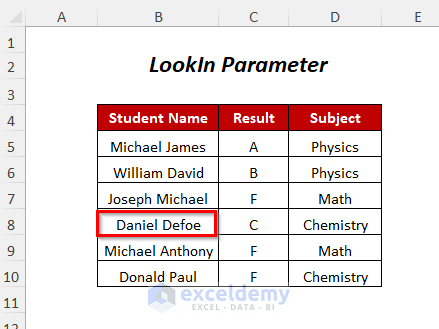
Steps
- Open a new VBA Module (see Method 1 for details).
- Insert the following code:
Sub FindwithLookIn()
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Sheets("LookIn").UsedRange.Find("Daniel Defoe", LookIn:=xlValues)
If Not rng Is Nothing Then
MsgBox rng.Address
Else
MsgBox "Not found"
End If
End Sub“Lookin” is the name of the sheet and “Daniel Defoe” is the string that you are looking for.
Here, LookIn:=xlValues will give the final value of a cell after the calculation.

- Press F5.
- You will get a Message Box containing the cell position of the string.
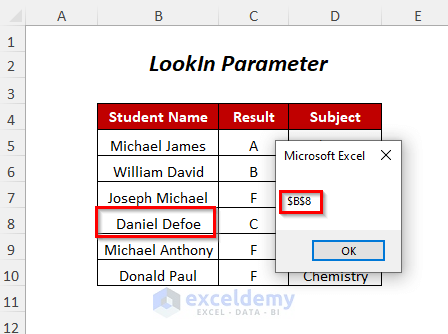
Method 4 – Finding a String With Look at Parameter
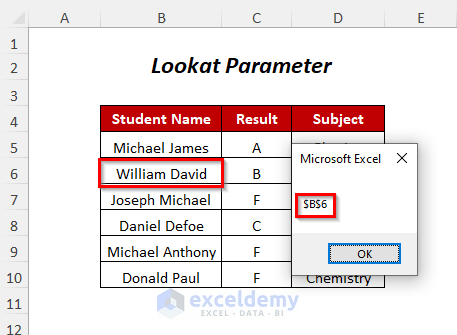
You can find the position of the student William David by using the Look at Parameter in your VBA code.
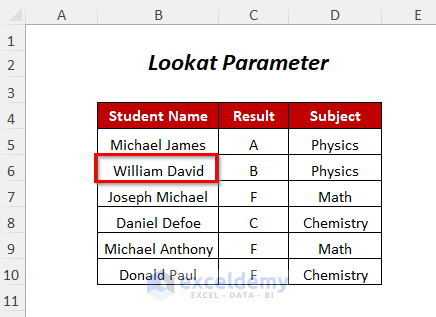
Steps
- Open a new VBA Module (see Method 1 for details).
- Insert the following code:
Sub FindwithLookat()
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Sheets("Lookat").UsedRange.Find("William", Lookat:=xlPart)
If Not rng Is Nothing Then
MsgBox rng.Address
Else
MsgBox "Not found"
End If
End Sub“Look at” is the name of the sheet and “William” is the string that you are looking for.
Here, Lookat:=xlPart will give the position of the string if it matches partially or fully (so, I have written here only “William”) but Lookat:=xlWhole will give the position of the string if it matches fully (in this case you have to write “William David”).

- Press F5.
- You will get the following Message Box containing the cell position of the student.
Method 5 – Finding a String With the SearchOrder Parameter
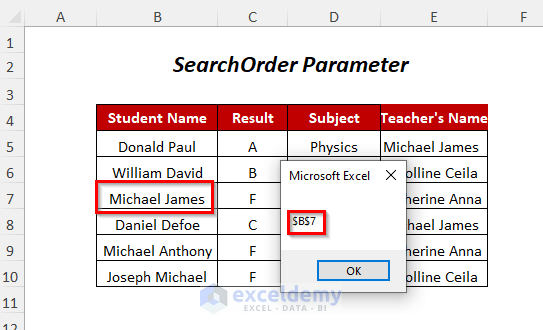
You can use the SearchOrder parameter to determine how the search will be carried out throughout the range to find the position of the student Michael James.

Steps
- Open a new VBA Module (see Method 1 for details).
- Insert the following code:
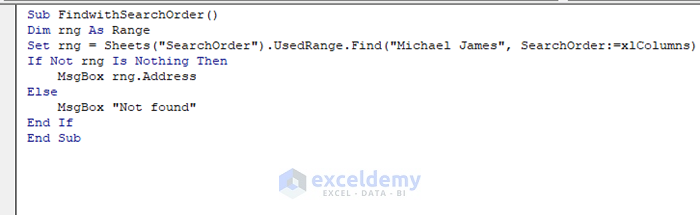
Sub FindwithSearchOrder()
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Sheets("SearchOrder").UsedRange.Find("Michael James", SearchOrder:=xlColumns)
If Not rng Is Nothing Then
MsgBox rng.Address
Else
MsgBox "Not found"
End If
End Sub“SearchOrder” is the name of the sheet and “Michael James” is the string that you are looking for.
SearchOrder:=xlColumns will search for the value column by column and return the position of the string that comes first in the column-wise serial.
- Press F5.
- You will get a Message Box containing the cell position of the student.
- Here’s an alternative code you can use:
Sub FindwithSearchOrder()
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Sheets("SearchOrder").UsedRange.Find("Michael James", SearchOrder:=xlRows)
If Not rng Is Nothing Then
MsgBox rng.Address
Else
MsgBox "Not found"
End If
End SubSearchOrder:=xlRows will search for the value row by row and return the position of the string that comes first in the row-wise serial.
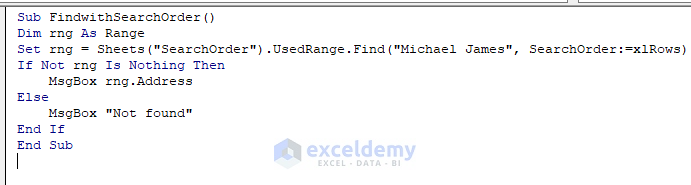
- You will get a Message Box containing the cell position of the teacher named “Michael James” (because the teacher’s name comes first in the row-wise direction).
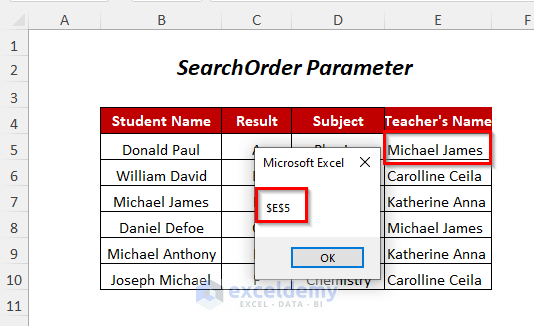
Method 6 – Finding a String With the SearchDirection Parameter
You can use the SearchDirection parameter to determine the search that will be carried out throughout the range in which direction to find the position of the marked name of the student Michael James.
Steps
- Open a new VBA Module (see Method 1 for details).
- Insert the following code:
Sub FindwithSearchDirection()
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Sheets("SearchDirection").UsedRange.Find("Michael James", SearchDirection:=xlNext)
If Not rng Is Nothing Then
MsgBox rng.Address
Else
MsgBox "Not found"
End If
End Sub“SearchDirection” is the name of the sheet and “Michael James” is the string that you are looking for.
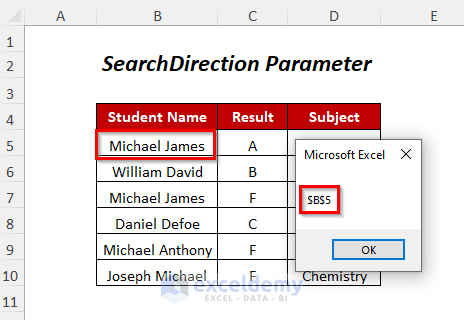
SearchDirection:=xlNext will start the search in the top left-hand corner of the data range and search downwards, so it will give the position of the string that comes first.

- Press F5.
- You will get a Message Box containing the cell position of the student named “Michael James” (serially first).
- You can try out the following code for variance in results:
Sub FindwithSearchDirection()
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Sheets("SearchDirection").UsedRange.Find("Michael James", SearchDirection:=xlPrevious)
If Not rng Is Nothing Then
MsgBox rng.Address
Else
MsgBox "Not found"
End If
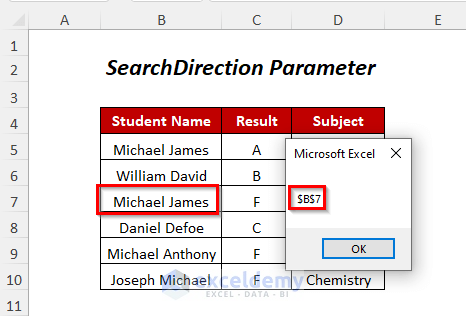
End SubSearchDirection:=xlPrevious will start the search in the bottom right-hand corner of the data range and search upwards, so it will give the position of the string that comes last.

- You’ll get the following Message Box containing the cell position of the student named “Michael James” (serially last).
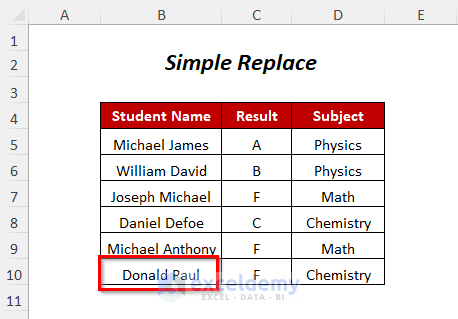
Method 7 – Replacing a String Without an Optional Parameter
Let’s replace Donald Paul with Henry Jackson in the Student Name column.
Steps:
- Open a new VBA Module (see Method 1 for details).
- Insert the following code:
Sub SimpleReplace()
Sheets("Simple Replace").UsedRange.Replace What:="Donald Paul", _ Replacement:="Henry Jackson"
End Sub“Simple Replace” is the name of the sheet “Donald Paul” is the string that you are looking for and “Henry Jackson” is the new name that you want to replace the previous one.
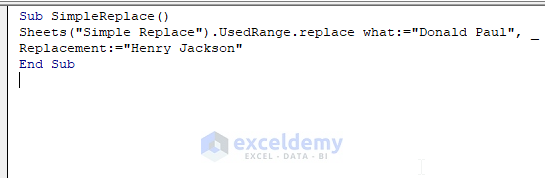
- Press F5.
- You will get the new name Henry Jackson in the position of Donald Paul.
Method 8 – Replacing a String With the REPLACE Function
Steps:
- Open a new VBA Module (see Method 1 for details).
- Insert the following code:
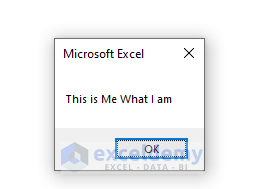
Sub FindReplace()
MsgBox Replace("This is You What I am", "You", "Me")
End Sub“You” will be replaced by “Me”

- Press F5.
- You will get the Message Box containing the replacement in the string.
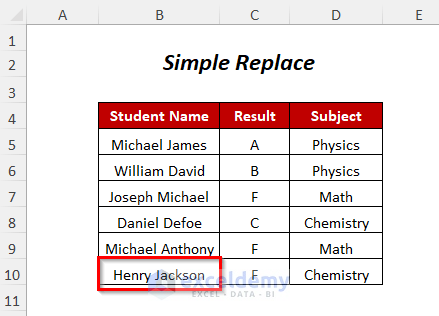
Method 9 – Find and Replace String for a Range of Data
We will replace Donald Paul with Henry Jackson in the Student Name column.
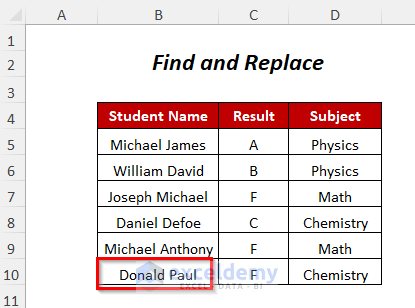
Steps:
- Open a new VBA Module (see Method 1 for details).
- Insert the following code:
Sub FindandReplace()
Dim rng As Range
Dim str As String
With Worksheets("Find and Replace").Range("B5:B10")
Set rng = .Find("Donald Paul", LookIn:=xlValues)
If Not rng Is Nothing Then
str = rng.Address
Do
rng.Value = Replace(rng.Value, "Donald Paul", "Henry Jackson")
Set rng = .FindNext(rng)
Loop While Not rng Is Nothing
End If
End With
End SubHere, “Find and Replace” is the sheet name “B5:B10” is the range of students’ names, “Donald Paul” is the student’s name which is to be found out, and then “Henry Jackson” will be the student’s name instead of the previous one.
WITH statement will avoid the repetition of the piece of code in every statement.
The IF statement will assign the item’s address to the str variable and the DO loop will replace all occurrences of the search word.

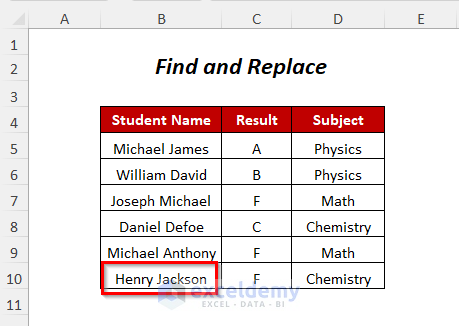
- Press F5.
- You will get the new name Henry Jackson instead of Donald Paul.
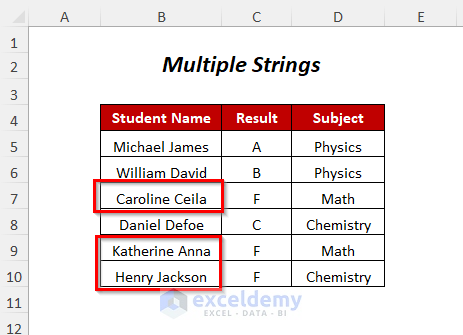
Method 10 – Find and Replace Multiple Strings Simultaneously
We will replace the names of three students Joseph Michael, Michael Anthony, and Donald Paul, with Caroline Ceila, Katherine Anna, and Henry Jackson, respectively.
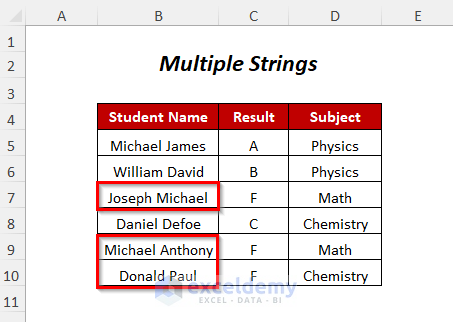
Steps:
- Open a new VBA Module (see Method 1 for details).
- Insert the following code:
Sub Multiplestrings()
Dim Sheet As Worksheet
Dim findlist As Variant
Dim repalcelist As Variant
Dim n As Long
Set Sheet = Sheets("Multiple Strings")
findlist = Array("Joseph Michael", "Michael Anthony", "Donald Paul")
replacelist = Array("Caroline Ceila", "Katherine Anna", "Henry Jackson")
For n = LBound(findlist) To UBound(findlist)
Sheet.Cells.Replace What:=findlist(n), Replacement:=replacelist(n), _
LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, MatchCase:=True, _
SearchFormat:=True, ReplaceFormat:=True
Next n
End Sub“Multiple Strings” is the sheet name, “Joseph Michael”, “Michael Anthony”, and “Donald Paul” are the students’ names to be found, and “Caroline Ceila”, “Katherine Anna”, and “Henry Jackson” will replace the previous names respectively.
The FOR loop will perform all of the replacements here.
- Press F5.
- You will get the new names in the sheet.
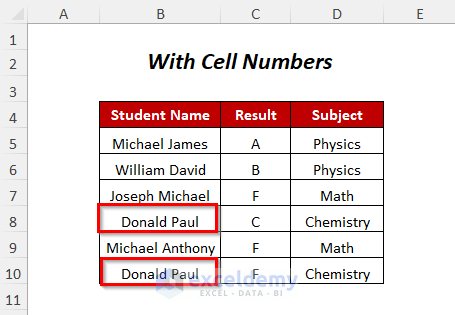
Method 11 – Find and Replace with the Numbers of Cells Changed
We will replace the student’s name Donald Paul with Henry Jackson and count the number of replacements.
Steps:
- Open a new VBA Module (see Method 1 for details).
- Insert the following code:
Sub CountingReplacedCells()
Dim Sheet As Worksheet
Dim fnd1 As Variant
Dim rplc1 As Variant
Dim Count As Long
fnd1 = "Donald Paul"
rplc1 = "Henry Jackson"
Set Sheet = Sheets("With Cell Numbers")
Count = Count + Application.WorksheetFunction.CountIf(Sheet.Cells, "*" & fnd1 & "*")
Sheet.Cells.replace what:=fnd1, Replacement:=rplc1, _
LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, MatchCase:=True, _
SearchFormat:=True, ReplaceFormat:=True
MsgBox "I have made total replacements in " & Count & " cell(s)."
End Sub“With Cell Numbers” is the sheet name, “Donald Paul” is the name to be found, and “Henry Jackson” will replace the previous name. Count will store the number of times the replacement occurs.
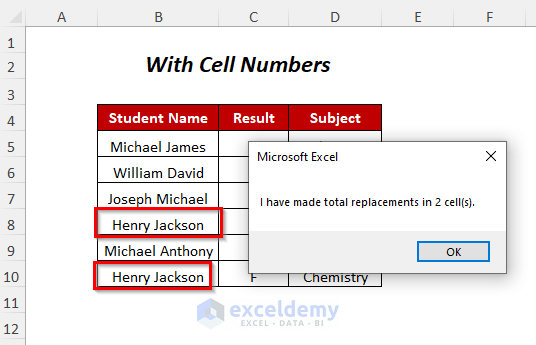
- Press F5.
- You will receive a Message Box that shows the total number of replacements.
Practice Section
We have included a practice section for each method.
Further Readings
- Excel VBA: How to Find and Replace Text in Word Document
- Excel VBA to Find and Replace Text in a Column
- Find and Replace a Text in a Range with Excel VBA
- Excel VBA to Replace Blank Cells with Text
- Excel VBA: Replace Character in String by Position
- Excel VBA: How to Replace Text in String



thank you your content is helpful
Hello, Kim!
Thanks for your appreciation. For more useful content visit our site ExcelDemy.
Regards
ExcelDemy