Method 1 – Format Cell Horizontally or Vertically with VBA
Excel’s CellFormat. The AddIndent property sets a Variable type value that indicates whether the text is automatically indented when the text alignment in a cell is set horizontally or vertically.
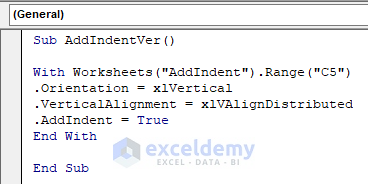
Sub AddIndentVer()
With Worksheets("AddIndent").Range("C5")
.Orientation = xlVertical
.VerticalAlignment = xlVAlignDistributed
.AddIndent = True
End With
End Sub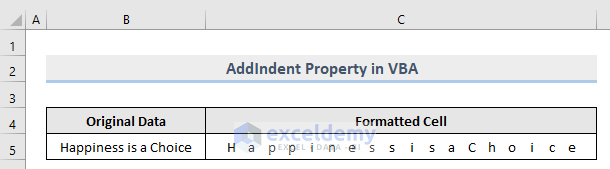
In our example, we formatted the cell in vertical alignment. But if you want to align the cell horizontally, then set Orientation = xlHorizontal and VerticalAlignment = xlHAlignDistributed
Method 2 – Format Alignment of Text in a Cell with Macro
2.1. Horizontal Alignment
If you want to align the text of a cell horizontally, then the VBA code is,
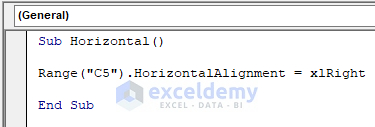
Sub Horizontal()
Range("C5").HorizontalAlignment = xlRight
End Sub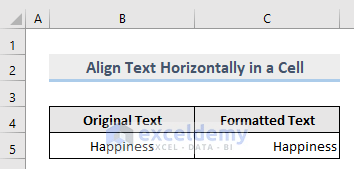
You can set the value of the property to any of the following constants according to your requirements,
- xlGeneral
- xlCenter
- xlDistributed
- xlJustify
- xlLeft
- xlRight.
2.2. Vertical Alignment
If you want to align the text of a cell vertically, then the VBA code is,
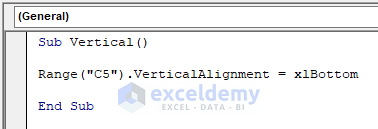
Sub Vertical()
Range("C5").VerticalAlignment = xlBottom
End Sub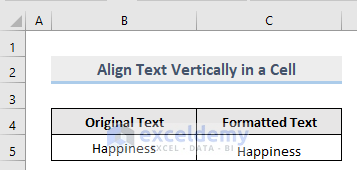
You can set the value of the property to any of the following constants according to your needs,
- xlBottom
- xlCenter
- xlDistributed
- xlJustify
- xlTop.
Method 3 – Format Borders of a Cell with VBA Code
You can format the borders of a cell according to your needs. The VBA code for this is,
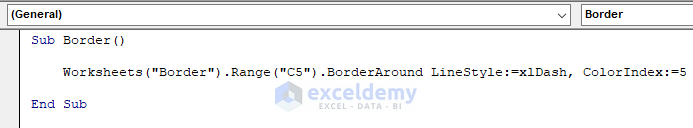
Sub Border()
Worksheets("Border").Range("C5").BorderAround LineStyle:=xlDash, ColorIndex:=5
End SubBorder Index
You can choose different borders for a single cell or cells of a range according to your needs using VBA.
- xlDiagonalDown: Border running from the upper left-hand corner to the lower right of each cell in the range.
- xlDiagonalUp: Border running from the lower left-hand corner to the upper right of each cell in the range.
- xlEdgeBottom: Border at the bottom of the range.
- xlEdgeLeft: Border at the left-hand edge of the range.
- xlEdgeRight: Border at the right-hand edge of the range.
- xlEdgeTop: Border at the top of the range.
- xlInsideHorizontal: Horizontal borders for all cells except borders on the outside of the range.
- xlInsideVertical: Vertical borders are for all the cells in the range except for the borders outside of the range.
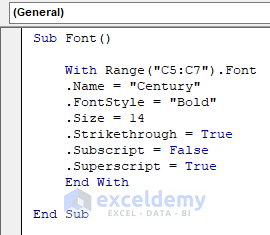
Method 4 – Format the Font of a Cell with VBA in Excel
You can format a cell’s name, style, size, color, effects, underlines, etc., using the VBA macro in the Excel worksheet.
The VBA code for that is,
Sub Font()
With Range("C5:C7").Font
.Name = "Century"
.FontStyle = "Bold"
.Size = 14
.Strikethrough = True
.Subscript = False
.Superscript = True
End With
End Sub 
Method 5 – Hide Cells of a Range in Excel with VBA
The FormulaHidden property sets a Variant type of value that indicates if the formula will be hidden when the worksheet is protected. The macro to do this is,
Sub HiddenFormula()
Worksheets("Sheet7").Range("B4:B6").FormulaHidden = True
End Sub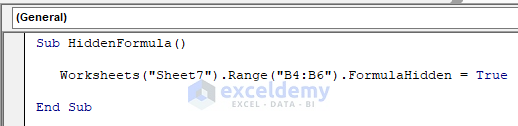
Method 6 – Change Indent Level for a Cell in Excel
IndentLevel sets an integer value between 0 and 15, representing the cell’s indent level or range.
The VBA code to format the indent level for a cell is,
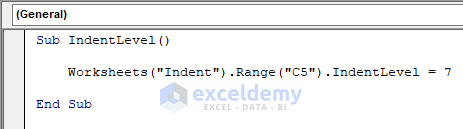
Sub IndentLevel()
Worksheets("Indent").Range("C5").IndentLevel = 7
End Sub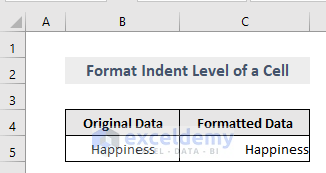
Method 7 – Change the Interior of a Cell in Excel
VBA code can set the interior of a cell, such as Color, Color Index, Pattern, Pattern Color, Pattern Color Index, Pattern Theme Color, Pattern Tint and Shade, Theme Color, Tint and Shade, etc.

Sub Interior()
If Not Range("C5").Interior.ThemeColor = ThemeColorLight2 Then
Range("C5").Interior.Pattern = xlPatternUp
End If
End Sub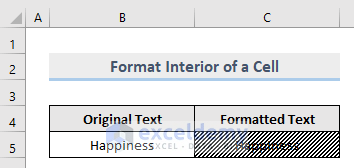
Method 8 – Excel’s Locked Property for Cells
This property returns True if the cell or range is locked and False if the value can be modified when the sheet is protected. When the specified range contains locked and unlocked cells, it returns Null. This property can also be used to lock or unlock cells.
The following VBA code locks cell B4:C4 on the Excel sheet “Locked” so that they can not be modified when the sheet is protected.
Sub LockCell()
Worksheets("Locked").Range("B4:C4").Locked = False
Worksheets("Locked").Protect
End SubMethod 9 – Merge Cells in Excel with Macro
If you want to merge cells in your Excel worksheet, set this property to True.
VBA macro to merge cells B8:D8 is,
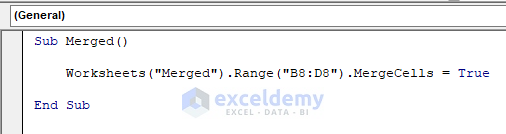
Sub Merged()
Worksheets("Merged").Range("B8:D8").MergeCells = True
End Sub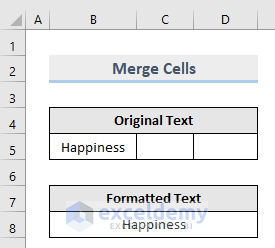
Method 10 – Format the Orientation of a Cell in Excel
Text orientation within the cell(s) can be set or returned by this property.
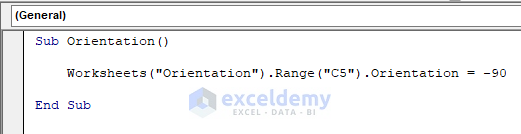
Sub Orientation()
Worksheets("Orientation").Range("C5").Orientation = -90
End Sub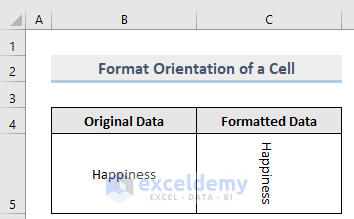
Its value can be any of the constants mentioned here,
- xlDownward
- xlHorizontal
- xlUpward
- xlVertical or
- an integer value from -90 to 90 degrees.
Method 11 – Format a Cell to Shrink to Fit in Excel
Excel’s ShrinkToFit property sets or returns a Variant type value to shrink automatically to fit the specified column width.
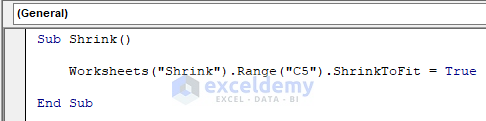
Sub Shrink()
Worksheets("Shrink").Range("C5").ShrinkToFit = True
End Sub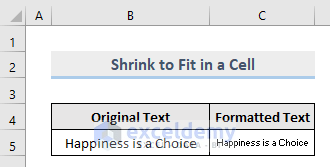
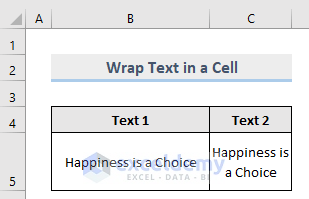
Method 12 – WrapText Property to Format Cell in Excel
This property returns True if the text is wrapped in cells within a specified range. It returns False if the text is not wrapped in all cells and Null if the specified range contains some wrapped texts and some unwrapped cells.
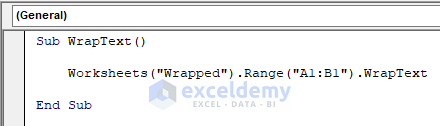
Sub WrapText()
Worksheets("Wrapped").Range("A1:B1").WrapText
End SubFor Instance, the following example will return Null in the Immediate window.
Download the Practice Workbook
You can download the free practice Excel workbook from here.
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!